Welcome to the Linkurious Enterprise administrator documentation. This documentation will help you install, run and customize Linkurious Enterprise.
Linkurious Enterprise is a three-tier application.
The presentation layer is a Web application. It uses our graph visualization library, Ogma, to allow rich interactions with the graph. It also provides a user interface to enable data administration and collaboration among end users.
The presentation layer communicates with the logic layer via a JSON-based REST API. Custom presentation layer application can be developed on top of the logic layer.
The logic layer is a NodeJS-based server. It provides a unified REST API to read, write and search into graph databases from multiple vendors (Neo4j, JanusGraph and Cosmos DB). It implements also a security layer with modular authentication that enables role-based access control policies. It can be connected to multiple graph databases at the same time and offers high-level APIs for collaborative exploration of graphs: users can create, share and publish graph visualizations, and multiple users can edit graph data.
Administrators can control it from its REST API for easy automation and deployment.
Multiple external authentication providers are supported (LDAP, Microsoft Active Directory, Microsoft Azure Active Directory, Google Suite, OpenID Connect, SAML2 / ADFS).
The data layer supports several graph databases, as well as indexation engines.

Consult with your vendor to make sure that your graph database is installed on appropriate hardware and configured for better performances:
Make sure that your graph database is secure:
Keep in mind that Linkurious Enterprise can be used without Elasticsearch, see search options.
If you are using Linkurious Enterprise with Elasticsearch
By default, SQLite is used for the user-data store. SQLite is not recommended for production environment: switch to MySQL/MariaDB/MSSQL instead.
Schedule regular backups of the user-data store:
Make sure your user-data-store database is secure
If you need high-availability, set up replication
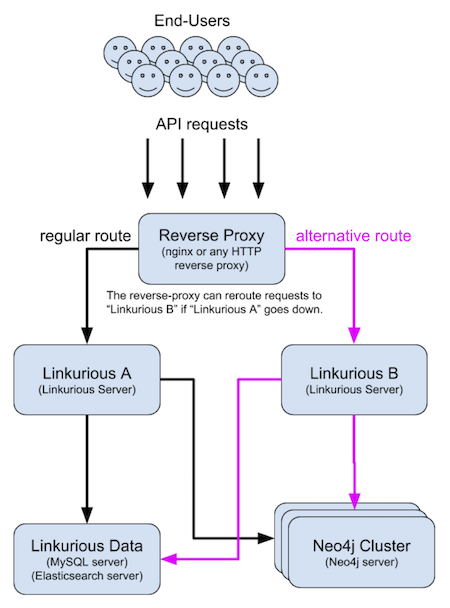
linkurious/data directoryforceHttps: true in Web Server configuration)Linkurious Enterprise can be set up with a backup instance to allow for continuity of service when the main server crashes.
For this setup:
A reverse proxy is then configured to send requests to the backup server when the main server is down. If you are using nginx, this sample configuration can be used:
http { # define the "backend" upstream upstream backend { # main server server linkurious-main.example.com; # backup server server linkurious-backup.example.com backup; } # redirect all queries to the "backend" upsteam server { location / { proxy_pass http://backend; } }}See nginx documentation for more details.
The user-data store database (containing visualizations, saved queries, user, groups, etc) is stored in a SQL database.
By default, this database is an SQLite database (located at linkurious/data/database.sqlite).
In production, the use of a MySQL/MariaDB/MSSQL database is recommended.
These databases can be located on a remote server.
The default user-data store (SQLite) is not encrypted.
Encryption is available with the following vendors:
Yes, when using an external user-data store (e.g. MariaDB, MySQL or MSSQL), the SQLite files can be deleted.
The configuration file contains all configurable options, as well as the configuration options of all configured data sources (e.g. User-Data Store host/port/username/encrypted password; Graph Database URL/username/encrypted password; Index Search URL/username/encrypted password, etc). All passwords/secrets in the configuration file are encrypted before storage.
The configuration file, like the rest of the data folder, should be considered private and not be readable by anyone other than the Linkurious Enterprise service account.
All application secrets stored by Linkurious Enterprise (Graph Database credentials, User-Data Store credentials, Index Search credentials, SSL certificate passphrase, etc.) are encrypted using the AES-256-CTR algorithm.
User passwords are strongly hashed before being stored in the database. Passwords for LDAP and other external authentication solutions are not stored at all.
The audit trail files are generated in linkurious/data/audit-trail by default.
This path can be set in the audit trail configuration.
The audit trail contains sensitive information and should be secured. It should be owned and readable only by the Linkurious Enterprise service account.
The data directory contains logs, configuration files, and, if enabled, audit trails. This information is sensitive, and the directory should be owned and readable only by the Linkurious Enterprise service account
A service account is an operating system user account with restricted privileges that is used only to run a specific service and own it data related to this service. Service accounts are not intended to be used by people, except for performing administrative operations. Access to service accounts is usually tightly controlled using privileged access management solutions.
Service accounts prevent other users and services from reading or writing to sensitive files in the directories that they own, and are themselves prevented from reading and writing to other parts of the file system where they are not owners.
We do not support Kerberos as of now (but we support many other third-party authentication services).
Linkurious Enterprise creates three types of logs:
data/logs/analytics.log): Usage telemetry (GDPR safe, not sensitive information)data/logs/linkurious.log and linkurious.exceptions.log): Server debugging logs (may contain graph queries).data/audit-trail/audit-trail.log): See audit trail log format details.If your LDAP server supports secure LDAP, use the "ldaps://" protocol in your LDAP configuration.
If you need authentication and transport layer security for Elasticsearch:
PEM (for Privacy-Enhanced Mail) is a file format for storing and sending cryptographic keys and certificates.
To verify if a certificate is PEM-encoded, open it with a text-editor, it should look something like this:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----MIICLDCCAdKgAwIBAgIBADAKBggqhkjOPQQDAjB9MQswCQYDVQQGEwJCRTEPMA0GA1UEChMGR251VExTMSUwIwYDVQQLExxHbnVUTFMgY2VydGlmaWNhdGUgYXV0aG9yDwEB/wQFAwMHBgAwHQYDVR0OBBYEFPC0gf6YEr+1KLlkQAPLzB9mTigDMAoGCCqGSM49BAMCA0gAMEUCIDGuwD1KPyG+hRf88MeyMQcqOFZD0TbVleF+UsAGQ4enAiEAl4wOuDwKQa+upc8GftXE2C//4mKANBC6It01gUaTIpo=-----END CERTIFICATE-----If you have a DER-encoded certificate (binary), it can be converted to PEM:
openssl x509 -inform der -in certificate.cer -out certificate.pemCrypto Shell Extensions)details tabCopy to file...NextBase-64 encoded X.509 (.CER) and click NextNextFinishMost graph vendors support search strategies other than Elasticsearch. See dails on our search options page.
Yes. See the geospatial configuration options for further details.
Yes, you can configure ArcGIS as the tile-server for geo-spatial mode. The ArcGIS documentation describes the API endpoints that is compatible with Linkurious Enterprise:
http://<MapServer-url>/tile/{z}/{y}/{x}For example:
./linkurious/start.sh: start the server./linkurious/stop.sh: stop the server./linkurious/menu.sh: open the management console./linkurious/menu.sh status: print the current status of the server./linkurious/menu.sh install: install as a system-wide service (requires root)./linkurious/menu.sh uninstall: remove from system-wide services (requires root)./linkurious/menu.sh help: show advanced optionsDepending on the configuration options specified, enabling the audit trail can have an impact on performance. See the audit trail documentation for details.
Linkurious Enterprise is a Web-application server. It needs to be installed on a server and can then be accessed by multiple users using their Web browser.
Technical requirements for the machine used to install the Linkurious Enterprise Web-application server:
Linkurious Enterprise hardware requirements change according to your needs and setup. Here are some scenarios with their suggested minimum hardware configurations.
Project up to 20 users and few alerts.
Using the embedded Elasticsearch1:
Not using the embedded Elasticsearch:
Project up to 100 users and tenth of alerts.
Using the embedded Elasticsearch1:
Not using the embedded Elasticsearch:
Project with more than 100 users and several alerts.
To maintain stable performance, it is necessary to move heavily loaded components to well-dimensioned dedicated servers/clusters:
Hardware requirements only for the Linkurious Enterprise server:
Linkurious Enterprise requires a 64-bit system to run.
1The embedded Elasticsearch is not recommended when dealing with large amounts of data, see Elasticsearch documentation.
2Some extra space is required for the Elasticsearch full-text index. This space is proportional to the size of your graph database. A (very) rough estimate could be 50% of your graph database (it also depends on the actual data density).
3It is possible to configure Elasticsearch for higher memory usage, please contact us at support@linkurio.us.
4It is possible to configure Linkurious Enterprise for higher memory usage more, please contact us at support@linkurio.us.
Please keep in mind that these technical requirements are for Linkurious Enterprise server only. For hardware requirements regarding your graph database, please refer to these guides:
Linkurious Enterprise includes an embedded Elasticsearch instance for search capabilities. Please keep in mind that this embedded instance will only work for smaller graphs (less than 50M nodes + edges). For larger graphs, you will need to deploy an Elasticsearch cluster. Please refer to Elasticsearch's hardware requirements guide for details.
Linkurious Enterprise server can be deployed on the following platforms:
Linkurious Enterprise embedded ElasticSearch engine requires Java 7 or Java 8 from Oracle or OpenJDK.
If you do not intend to use the embedded ElasticSearch you need to change the configuration file choosing a different indexation strategy for all the configured datasources. With this configuration, the embedded Elasticsearch won't be started and the Java version won't be checked.
You can download the latest JRE from Oracle's website.
Installation instructions:
The JAVA_HOME environment variable should be set.
In order to use the embedded ElasticSearch on Windows 10, we strongly recommend using Java 8u211 as some other versions are incompatible with our embedded ElasticSearch.
Linkurious Enterprise uses an embedded SQLite store for user-data persistence. This database requires GLIBC >= 2.14. Some older Linux distributions don't have this version of GLIBC available. You can check the version available on your system on http://distrowatch.com.
If SQLite does not work on your system, please refer to the user-data store documentation section to learn how to use an alternative database.
Technical requirements for users that access Linkurious Enterprise with their Web browser:
Hardware requirements of the Linkurious Enterprise Web client vary with the size of the visualized graphs. For up to 500 nodes and edges in a single visualization, we recommend to use a machine with 4 GB RAM, and 2 CPU cores @ 1.6 Ghz.
The minimal screen resolution is 1024 x 768.
End-users will access Linkurious Enterprise through a Web browser. The following browsers are officially supported:
The latest version of Linkurious Enterprise can be downloaded from https://get.linkurio.us/.
Log in with the username and password created during the purchase process and then go to the download section for the specific license (in case of multiple one), it will be possible to download the package for the correct platform.
The ZIP file contains:
Please see the Linkurious Enterprise version compatibility matrix and our documentation on how to update Linkurious Enterprise.
To work properly, Linkurious Enterprise only need permissions (including write access) on the whole application directory, no administrative rights are needed.
The only exception may be related to Operating Systems' security policies preventing any standard user to bind applications on the first 1024 port numbers, see web server configuration to learn more on the issue and how prevent to grant administrative rights.
As best practice, it is advised to create a dedicated service account (e.g. linkurious)
with the minimum level of permissions.
> unzip linkurious-linux-v2.9.14.zip> cd linkurious-linuxlinkurious-linux/data/config/production.json (see how to configure a data-source)java -version in a terminal), if needed, install JavaSee how to start Linkurious Enterprise on Linux.
linkurious-windows folderlinkurious-windows/data/config/production.json (see how to configure a data-source)See how to start Linkurious Enterprise on Windows.
> unzip linkurious-osx-v2.9.14.zip> cd linkurious-osxlinkurious-osx/data/config/production.json (see how to configure a data-source)java -version in a terminal), if needed, install JavaSee how to start Linkurious Enterprise on Mac OS X.
> docker load -i linkurious-docker-v2.9.14.tar.gzSee how to start Linkurious Enterprise with docker.
In order to run Linkurious Enterprise automatically when the operating system starts, it is possible to install it as a system service on Linux, Mac OS X and Windows.
Open the administration menu by running menu.sh, menu.bat or menu.sh.command in the Linkurious Enterprise folder.
Click on Install Linkurious as a system service (administrative rights may be needed to successfully complete the task).
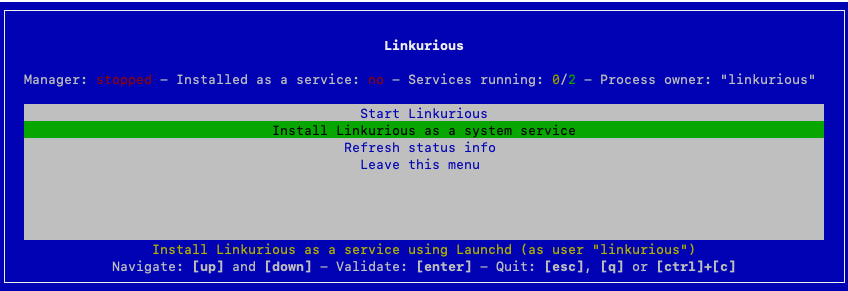
Linkurious Enterprise automatically detects the owner of the folder and will use that user as the
Process owner.It is possible to use a different user by running the
menuscript with the option--user=USER(whereUSERis the desiredProcess ownerwith adequate permissions).
When Linkurious Enterprise is installed as a service, the administration menu (by running menu.sh,
menu.bat or menu.sh.command in the Linkurious Enterprise folder) will show the current status
of the service as well as a new entry to Uninstall Linkurious from system services.
To start Linkurious Enterprise, run the start.sh script in the linkurious-linux directory.
Alternatively, run the menu.sh script and click Start Linkurious.
By default, Linkurious Enterprise server will listen for connection on port 3000.
However, some firewalls block network traffic ports other than 80 (HTTP).
See the Web server configuration documentation to learn how to make Linkurious Enterprise listen on port 80.
To start Linkurious Enterprise, run the start.bat script in the linkurious-windows directory.
Alternatively, run the menu.bat script and click Start Linkurious.
The firewall of Windows might ask you to authorize connections to Linkurious Enterprise. If so, click on Authorize access.
Content of the linkurious-windows directory:
Linkurious Enterprise starting up on Windows:
To start Linkurious Enterprise, run the start.sh.command script in the linkurious-osx directory.
Alternatively, run the menu.sh.command script and click Start Linkurious.
The Linkurious Enterprise docker image exposes the ports 3000 and 3443 for http and https connections respectively.
These ports should we mapped on the host machine to allow user connections.
Please visit the docker documentation to learn how publish the ports of a container.
Even if not strictly necessary, the best practice is to define external named volumes to store application data outside the container.
The Linkurious Enterprise docker image doesn't declare any volume, however below folders should be maintained when upgrading Linkurious Enterprise and therefore should be mapped to external volumes:
/data stores Linkurious Enterprise configuration, logs and application data./elasticsearch stores the Embedded ElasticSearch data.Please visit the docker documentation to learn how the configure volumes.
Here is an example to create named volumes (an arbitrary name can be chosen):
docker volume create lke-datadocker volume create lke-elasticsearchNow you need to install your Linkurious Enterprise license:
lke-data in our example).license.key file located inside the folder linkurious-windows/data.lke-data in our example).To start a Linkurious Enterprise docker image, please use the docker run command.
Here is an example:
docker run -d --rm \ -p 3000:3000 \ --mount type=volume,src=lke-data,dst=/data \ --mount type=volume,src=lke-elasticsearch,dst=/elasticsearch \ linkurious:2.9.14If you choose to mount a host machine folder as a volume please make sure that the user within the container has read and write access to the volume folders. You can do that by adding a
--useroption to the docker run command. Please read the docker documentation to learn more.
Here is an example:
docker run -d --rm \ -p 3000:3000 \ --mount type=bind,src=/path/to/my/data/folder,dst=/data \ --mount type=bind,src=/path/to/my/elasticsearch/folder,dst=/elasticsearch \ --user linkurious:1000 \ linkurious:2.9.14Please read the previous section on starting a Linkurious Enterprise instance using docker, and the section on fault tolerance.
A simple way to test out Linkurious Enterprise using kubernetes is to create a simple deployement, using only one replica, and allocate a PersistentVolume for both of the volumes (lke-data, lke-elasticsearch) described above.
In production however you would want to follow the fault tolerance guide and use a StatefulSet, with a main/failover strategy, and the appropriate strategy configured for your load-balancer or ingress.
Run the stop.sh script in the linkurious-linux directory.
Alternately, run menu.sh and click Stop Linkurious.
Run the stop.bat script in the linkurious-windows directory.
Alternately, run menu.bat and click Stop Linkurious.
Run the stop.sh.command script in the linkurious-osx directory.
Alternately, run menu.sh.command and click Stop Linkurious.
To edit the Linkurious Enterprise configuration, you can either edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json
or use the Web user-interface:
Using an administrator account, access the Admin > Configuration menu to edit the Linkurious Enterprise configuration:
Some configuration change requires a restart to be applied. Linkurious Enterprise will notify you about it and offer you to restart from the Web UI only if you made the changes from the Web UI itself. If you modified the production.json file manually, changes won't get applied immediately and you will need to restart Linkurious Enterprise.
Configuration keys are divided by category. When you are finished changing, click Save.
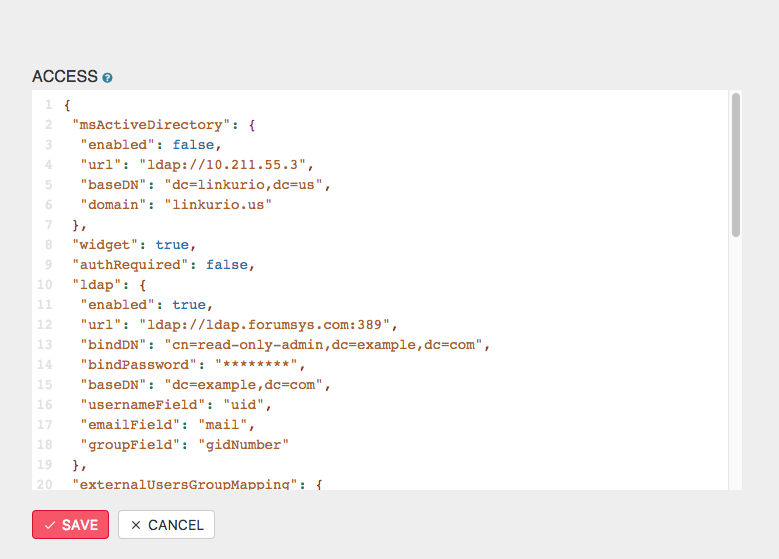
Password fields will always be hidden from the Web UI, but they can be edited.
Release Date: 2021-03-08
| Feature \ Vendor | Neo4j | JanusGraph | JanusGraph on IBM Compose | Cosmos DB |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Full-text search | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Graph styles customization | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Graph filtering | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Graph editing | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Access rights management | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Custom graph queries | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Custom query templates | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ |
| Alerts | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ |
| Shortest path analysis | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ |
Linkurious Enterprise starts 3 separate processes when launched:
node (or node.exe): The internal process managernode (or node.exe): The Linkurious Enterprise Server processjava (or java.exe): The embedded Elasticsearch indexation server (if enabled).Check if these processes are alive by opening the menu from the Linkurious Enterprise directory (see how to open it on each operating system below):
Run menu.sh. Alternately, run menu.sh status.
Run menu.bat. Alternately, run menu.bat status.
Run menu.sh.command. Alternately, run menu.sh.command status.
The status of the API can be retrieved using a browser or a command line HTTP client like cURL.
To retrieve the API status, send a GET request to http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/status
(replace 127.0.0.1 and 3000 with the actual host and port of your server).
// example response "status": "code": 200 "name": "initialized" "message": "Linkurious ready to go :)" "uptime": 8633 To retrieve the API status, send a GET request to http://127.0.0.1:3000/api/version
(replace 127.0.0.1 and 3000 with the actual host and port of your server).
// example response "tag_name": "2.9.14" "name": "Brilliant Burrito" "prerelease": false "enterprise": trueThe logs of the application are located in linkurious/data/manager/logs folder:
linkurious-server.log: Linkurious Enterprise server outputembedded-elasticsearch.log: embedded Elasticsearch outputFor a structured version of the Linkurious Enterprise server logs in JSONL format, see the linkurious/data/logs folder:
linkurious.log: Linkurious Enterprise server general log, with timestampslinkurious.exceptions.log: Linkurious Enterprise server exceptions log, with timestampsIf you need to get support regarding an issue or you have a question, please contact us at support@linkurio.us.
If the issue is technical, send us the application logs as described below.
You can download an automatically generated report from the Web user interface via the Admin > Global configuration menu:
At the end of the page, click Download Report:

It can happen that the system fails to start due an error. Since the impossibility to download the automatically generated report, the following files should be added manually to a compressed archive:
The application logs: the manager and log folders stored in <linkurious-installation>/data
The application configuration (optional): the production.json file stored in <linkurious-installation>/data/config
Depending on your situation, the configuration file (
production.json) may sometimes contains clear-text passwords. Consider redacting such password before sharing your configuration with the support team.
Before starting to explore the content of your graph database using Linkurious Enterprise, you need to import data in your graph database.
The following sections will help you import data into your graph:
If you already have data in your graph database or you don't need to import anything, see how to configure your graph database with Linkurious Enterprise.
Linkurious relies on Neo4j to store the data. The data importation is thus not handled by our solution. Many options exist to import data into Neo4j:
Finally, if you want to quickly try Linkurious Enterprise with an example dataset, you can download a Neo4j-compatible example dataset.
Please refer to the JanusGraph online documentation for details on how to load data into JanusGraph.
Please refer to the Cosmos db online documentation for details on how to load data into Cosmos db.
We release a new version of Linkurious Enterprise every couple of month on average. New releases include new features, improvements, and bug fixes.
The following pages will help you check for updates, back-up Linkurious Enterprise before updating, and update Linkurious Enterprise.
Using an administrator account, access the Your Username > About menu to open the Linkurious Enterprise info:
Click Check for updates to see if you are using the latest version.
Alternatively, you can check at http://linkurio.us/version/linkurious-enterprise.json
// example response "tag_name": "v2.9.14" // latest version of Linkurious Enterprise "message": null "url": "https://get.linkurio.us/" // where to download the latest version from Follow these steps to perform a backup of your Linkurious Enterprise data:
linkurious/data folderPlease note that this procedure does not back-up your graph data, but only your Linkurious Enterprise configuration and user-data (visualizations, users, etc.).
If you follow this procedure, you will be able to update Linkurious Enterprise to a newer version without loosing your configuration and user-data store. You data will be automatically migrated to the newer version.
Before updating, make sure that you have backed-up your data in case something unexpected happens.
During the update procedure, if Linkurious Enterprise is running, it will be stopped. You will need to re-start Linkurious Enterprise after the update procedure.
linkurious-xxx-v2.9.14.zip in your current Linkurious Enterprise directory (along the start stop and update scripts)update.sh, OSX: update.sh.command, Windows: update.bat)If you use the Linkurious Enterprise docker image, the only step to update Linkurious Enterprise is to use the new docker image with the existing Linkurious Enterprise data volume.
If the update script fails, please check the update log located
at linkurious/data/update.log for details.
A data-source is a conceptual representation of a graph database within Linkurious Enterprise. Visualizations and other user data created within Linkurious Enterprise will be associated their respective data-source.
Every data-source is uniquely identified with a sourceKey,
a string computed from the url and the store id of the database.
Modifying the url or regenerating a database will result in Linkurious Enterprise generating a new sourceKey, consequently creating a new data-source with new information.
If this behaviour is not desirable, consider using a stable sourceKey.
By default, Linkurious Enterprise is configured to connect to a Neo4j database at 127.0.0.1:7474.
Linkurious Enterprise can connect to some of the the most popular graph databases:
Linkurious Enterprise is able to connect to several graph databases at the same time and lets you switch from one database to another seamlessly.
You can configure your data-sources via the Web user interface
or directly on the linkurious/data/config/production.json file.
Using an administrator account, access the Admin > Data menu to edit the current data-source configuration:
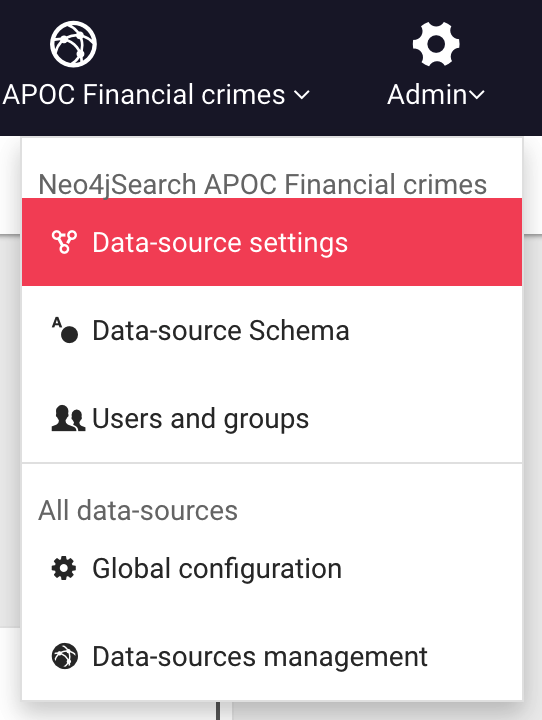
Edit the data-source configuration to connect to your graph database:
Submit the changes by hitting the Save configuration button.
Edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
See details for each supported graph database vendor:
Neo4j v4 is partially supported in Linkurious Enterprise 2.9.14.
The following Neo4j v4 features are currently not supported:
Neo4j is supported since version 3.2.0.
Note that Neo4j 4.0.0 and 4.0.1 are not supported. Neo4j 4 is supported since version 4.0.2.
To edit the Neo4j data-source configuration,
you can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474/" "user": "myNeo4jUser" "password": "nyNeo4jPassword" "index": "vendor": "neo4jSearch" Linkurious can connect to Neo4j via the
Boltprotocol. To do so, you need to enable the protocol in your Neo4j configuration file. If Linkurious is connected over HTTP/S, it will try to automatically upgrade the connection to Bolt. The HTTP/S protocol is still required to perform a small subset of operations.
Supported graphdb options with Neo4j:
url (required): URL of the Neo4j server (HTTP / HTTPS / bolt / neo4j)user (optional): Neo4j user (if credentials are enabled, see Neo4j credentials)password (optional): Neo4j password (if credentials are enabled)proxy (optional): URL of the HTTP proxy to use to connect to Neo4j (only used when url is HTTP/S)alternativeNodeId (optional): Name of the node property to use as reference in visualizations (see alternative IDs)alternativeEdgeId (optional): Name of the edge property to use as reference in visualizationslatitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for latitude (used in geo mode)longitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for longitude (used in geo mode)allowSelfSigned (optional, default false): Whether to allow self-signed certificatesdatabaseName (optional for v4.x.x): Name of the database to be connectedallowVirtualEntities (optional, default true): Whether to allow virtual nodes and virtual edgesalternativeURLs (optional for v4.x.x): Linkurious accepts a string array consisting of alternative Neo4j Bolt URLs for high availability.httpUrl (optional): Neo4j HTTP url needed to connect with a "architect" userFor Neo4j v4 and later, LKE provides full support for Neo4j connections over Bolt.
LKE will use Full Bolt connector when it is provided with any of following
urlprefixes:bolt,neo4j,neo4j+s
It is recommended to use Full Bolt connector for Neo4j v4 and later.
LKE allows using Neo4j instances running on Neo4j Aura as data-sources.
Neo4j Aura is only supported for the Neo4j Aura instances running Neo4j engine v4.0 and later.
In order to have full-text search, you can choose among the following options:
If you just installed Neo4j, these steps will help you create credentials:
Alternatively, you can disable credentials in Neo4j by editing the Neo4j configuration at neo4j/conf/neo4j.conf
by uncommenting the following line:
dbms.security.auth_enabled=falseNote that Linkurious requires a Neo4j user with the Neo4j built-in
adminorarchitectrole. This is needed so that Linkurious can use Neo4j features like Index creation and Query cancellation.
If you are connecting via an architect role to Neo4j 3.5, it's necessary to explicitly specify both the bolt url and the http url via the url and httpUrl configuration keys respectively.
Configure altenative ids indices is only possible starting from Neo4j 3.5.1 and it's recommended to do so.
The first step is to:
myAlternativeNodeIdIndex['Company', 'Person']myUniqueNodeIdOnce we have this information we can create the indices with the following Cypher queries:
call db.index.fulltext.createNodeIndex('myAlternativeNodeIdIndex', ['Company', 'Person', 'City'], ['myUniqueNodeId'], {analyzer: 'keyword'})
call db.index.fulltext.createRelationshipIndex('myAlternativeEdgeIdIndex', ['WORKS_FOR', 'LIVES_IN'], ['myUniqueEdgeId'], {analyzer: 'keyword'})
If new node labels or edge types are added to Neo4j, it's necessary to recreate these indices with the full list of categories.
Once the indices are created, we can configure them Linkurious:
Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474/" "user": "myNeo4jUser" "password": "nyNeo4jPassword" "alternativeNodeId": "myUniqueNodeId" "alternativeNodeIdIndex": "myAlternativeNodeIdIndex" "alternativeEdgeId": "myUniqueEdgeId" "alternativeEdgeIdIndex": "myAlternativeEdgeIdIndex" "index": "vendor": "neo4jSearch" JanusGraph is supported since version 0.1.1.
To edit the JanusGraph data-source configuration,
you can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "janusGraph" "url": "ws://127.0.0.1:8182/" "graphAlias": 'graph1' "traversalSourceAlias": "g1" "index": "vendor": "janusGraphSearch" "create": true Supported graphdb options for JanusGraph:
url (required): URL of the Gremlin server (must be a WebSocket URL, i.e. start with ws:// or wss://)graphAlias (required): Name of the remote graph instance, alias graphtraversalSourceAlias (optional, default g): Name of the corresponding traversal source instance, alias gconfiguration (alternative configuration): Dictionary of configuration values (for reference, see the JanusGraph documentation)configurationPath (alternative configuration): Path to the Gremlin configuration file on the Gremlin serveruser (optional): JanusGraph userpassword (optional): JanusGraph passwordalternativeNodeId (optional): Name of the node property to use as reference in visualizations (see alternative IDs)alternativeEdgeId (optional): Name of the edge property to use as reference in visualizationslatitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for latitude (used in geo mode)longitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for longitude (used in geo mode)allowSelfSigned (optional, default false): Whether to allow self-signed certificatesThere are 3 alternatives to configure JanusGraph:
graphAlias and traversalSourceAlias fieldsconfiguration field in json formatconfigurationPath fieldNote that only one of these alternatives can be used.
You can access your dynamically created graphs using the graph and traversal bindings references.
Simply set graphAlias to <graph.graphname> and traversalSourceAlias to <graph.graphname>_traversal.
Visit the JanusGraph Documentation for more information on how to set up dynamic graphs.
Linkurious DOES NOT support JanusGraph versions above 0.3.0 with the default configuration.
However, you can connect to a JanusGraph 0.3+ instance by modifying the default serializer configuration.
To do this, follow these steps:
$INSTALL_DIR/conf/gremlin-server/gremlin-server.yaml for JanusGraph versions 0.4 and below.$INSTALL_DIR/conf/gremlin-server/gremlin-server-cql-es.yaml for JanusGraph versions 0.5 and above.serializers: - { className: org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.ser.GraphSONMessageSerializerGremlinV1d0, config: { ioRegistries: [org.janusgraph.graphdb.tinkerpop.JanusGraphIoRegistryV1d0] }} - { className: org.apache.tinkerpop.gremlin.driver.ser.GraphSONMessageSerializerV1d0, config: { ioRegistries: [org.janusgraph.graphdb.tinkerpop.JanusGraphIoRegistryV1d0] }}In order to have full-text search, you can choose among the following options:
Linkurious can connect to your JanuGraph instances deployed on Compose.
Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "janusGraphForCompose" "url": "wss://xyz.composedb.com:16916" "user": "admin" "password": "XYZ" "graphName": "myGraph" "index": "vendor": "elasticSearch" "host": "127.0.0.1" "port": 9201 Supported graphdb options for JanusGraph For Compose:
url (required): URL of the Gremlin server provided by Compose (must be a WebSocket URL, i.e. start with ws:// or wss://)user (optional): JanusGraph userpassword (optional): JanusGraph passwordgraphName (required): Name of the graph to usecreate (optional): true to let Linkurious create the repository if it does not existalternativeNodeId (optional): Name of the node property to use as reference in visualizations (see alternative IDs)
alternativeEdgeId (optional): Name of the edge property to use as reference in visualizationslatitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for latitude (used in geo mode)longitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for longitude (used in geo mode)allowSelfSigned (optional, default false): Whether to allow self-signed certificatesCosmos DB is supported by Linkurious.
To edit the Cosmos DB data-source configuration,
you can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "cosmosDb" "url": "https://your-service.gremlin.cosmosdb.azure.com:443/" ".NET SDK URI": "https://your-service.documents.azure.com:443/" "database": "your-graph-database" "collection": "your-collection" "primaryKey": "your-account-primary-key" "partitionKey": "your-collection-partition-key" "index": "vendor": "azureSearch" "url": "https://your-search-service.search.windows.net" "apiKey": "your-search-service-admin-api-key" "nodeIndexName": "your-node-index" "edgeIndexName": "your-edge-index" Supported graphdb options for Cosmos DB:
url (required): This is the full Gremlin Endpoint of your Cosmos DB. Should not to be confused with the .NET SDK URI.NET SDK URI (required): The .NET SDK URI of your Cosmos DBdatabase (required): Cosmos DB databasecollection (required): Cosmos DB collectionprimaryKey (required): Cosmos DB account primary keypartitionKey (required): The partition key of your Cosmos DB collectionalternativeNodeId (optional): Name of the node property to use as reference in visualizations (see alternative IDs)alternativeEdgeId (optional): Name of the edge property to use as reference in visualizationslatitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for latitude (used in geo mode)longitudeProperty (optional): Name of the node property to use for longitude (used in geo mode)allowSelfSigned (optional, default false): Whether to allow self-signed certificatesIn order to have full-text search, you can choose among the following options:
When you save a visualization in Linkurious Enterprise, only the node and edge identifier are persisted in the user-data store, along with position and style information. When a visualization is loaded, the node and edge identifiers are used to reload the actual node and edge data from the graph database.
If you need to re-generate your graph database from scratch, the graph database will probably generate new identifiers for all nodes and edges, breaking all references to nodes and edges in existing visualizations.
You can configure Linkurious Enterprise to use a node or edge property as stable identifiers. Once set-up, Linkurious Enterprise will use the given property as identifier instead of using the identifiers generated by the database.
Thank to this strategy, visualizations will be robust to graph re-generation.
Notice that the properties used as identifier should be indexed by the database to allow for a fast lookup by value.
To use alternative node and edge identifiers,
edit your data-source database configuration in the configuration file (linkurious/data/config/production.json):
Example of alternative identifier configuration with Neo4j:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474/" "alternativeNodeId": "STABLE_NODE_PROPETY_NAME" "alternativeEdgeId": "STABLE_EDGE_PROPETY_NAME" // [...] Configuring alternative ids indices is only possible with Neo4j 3.5.1 and above. If you plan on using a compatible Neo4J version and alternative ids, we recommend configuring alternative ids indices.
To achieve better performance with alternative Ids is recommended to configure indices for alternative node and edge Ids.
Refer to the documentation specific to Neo4j on how to configure these indices.
Linkurious Enterprise generates a unique identifier for data-source, based on internal information from the data-source.
This data-source identifiers (called the sourceKey) is used to identify all user-data (visualizations etc.)
that belongs to a data-source.
When re-generating a Neo4j graph database, for example, the sourceKey will change.
In order to avoid breaking all references to existing visualizations,
it is possible to set manually the sourceKey of a data-source.
Before re-generating the graph database, go to the Admin > Sources menu:
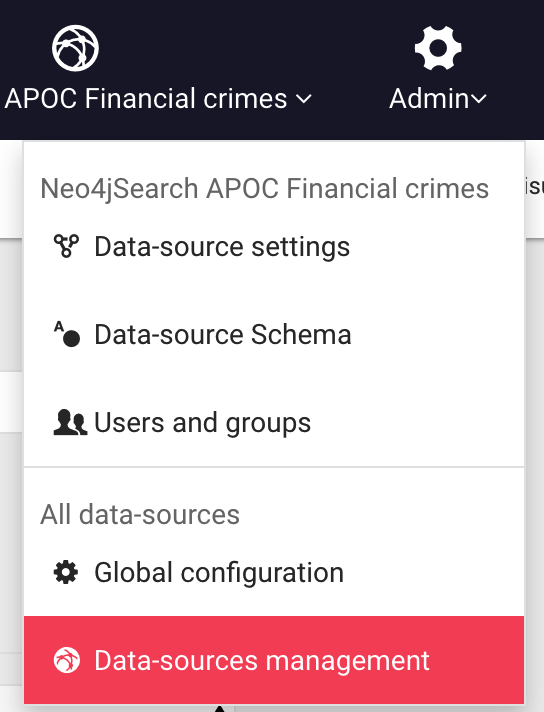
In the sources administration panel, find the Key value for your data-source (e.g. 1c3490bd) and copy it.
Then, edit the configuration file (linkurious/data/config/production.json)
and set the key manualSourceKey for your data-source:
"dataSources": "manualSourceKey": "1c3490bd" "graphdb": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474/" // [...] We recommend using a manual sourceKey if you need to re-generate a database with existing user data (visualizations etc.), or when the hostname and port number of your data-source are likely to change after the first connection to Linkurious Enterprise.
Alternatively, you have the possibility to merge the data-sources directly from the data-source management page with the following steps:
From the dashboard, go to the Admin > Data-sources management menu
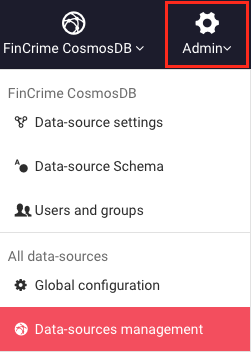
The data-source to be merged should be the old data-source now marked as offline because it has been replaced with the freshly generated data-source.
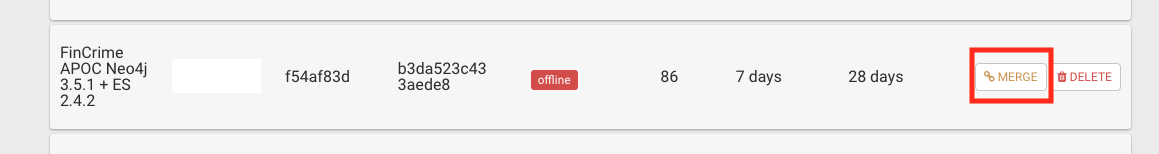
On the resulting modal, select the new data-source then click on the merge button.
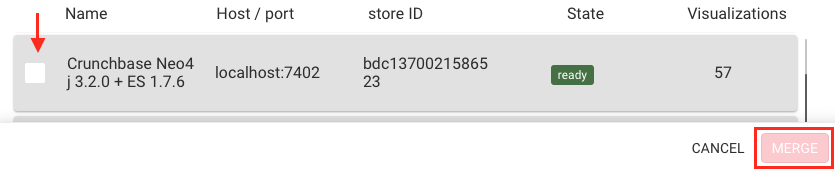
The user can choose to perform a normal merge, or an overwrite merge.
As a result, the following objects from the old data-source will be merged in the new data-source:
The Data-Source won't be deleted in case the user decides to do an overwrite merge at a later stage.
To perform an overwrite merge simply select the overwrite check box in the merge modal.
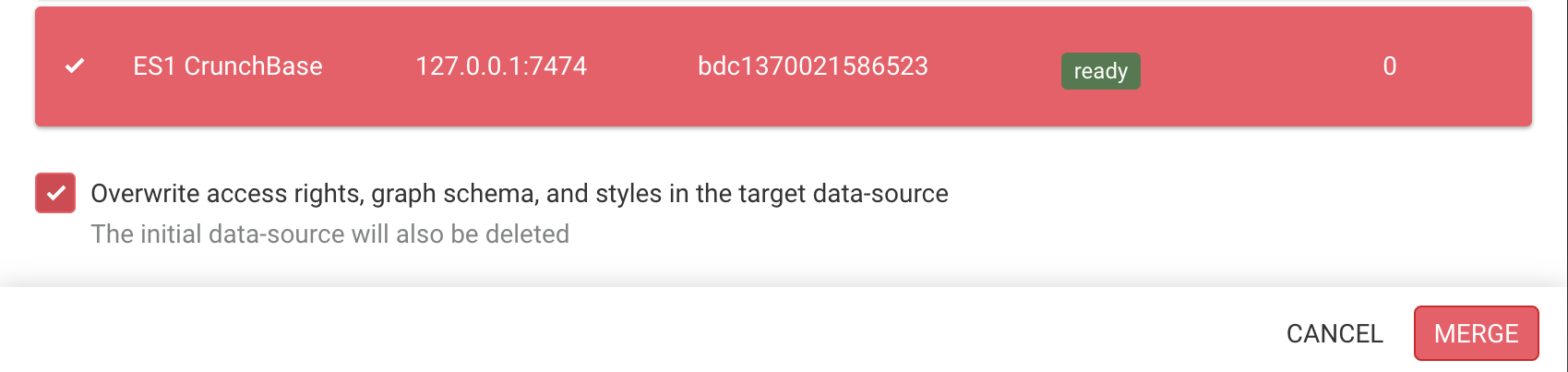
As a result, the objects from the old data-source mentioned above will be merged in the new data-source. Additionally, the following objects will be replaced in the new data-source with the ones from the old data-source:
This action will irreversibly remove any data associated with the old data-source, and the data-source will be deleted.
The following advanced data-source settings applies to all data-sources.
To change them, see how to configure Linkurious Enterprise.
connectionRetries (default: 10): The maximum number of connection attempts to each data-source and to the search engine before stating them as disconnected.
maxConnectionTimeout (default: 60000): The maximum time in milliseconds before the connection attempt to each data-source times out.
pollInterval (default: 10): Check if the data-sources and search engine are connected at each interval (in seconds).
defaultTimezone (default: Z): The timezone in which to represent date and datetime values
timeline (default: false): Whether the visualization timeline is available in the workspace UI
layoutWorkers (default: 2): Number of processes dedicated to computing server-side the layout of visualizations (Currently only available via Linkurious APIs)
indexationChunkSize (default: 5000): The number of nodes and edges retrieved at each batch during the indexation of the graph database.
searchAddAllThreshold (default: 500): The maximum number of search results that the user can add to a Visualization at once.
minSearchQueryLength (default: 3): The number of characters needed to trigger a search query. Set 1 to provide live results from the first character typed by the user.
searchPrefixExpansion (default: true): Whether Linkurious should return nodes and edges that contain the search query as a prefix, e.g.: Searching Link will return node Linkurious.
supernodeThreshold (default: 10000): Number of adjacent edges after which a node is considered a supernode.
edgesBetweenSupernodes (default: false): Whether Linkurious should retrieve edges between 2 supernodes. Note: Linkurious always return edges between a supernode and a regular node.
rawQueryTimeout (default: 60000): Milliseconds after which a query to the database will time out.
defaultFuzziness (default: 0.1): Default value to search fuzziness between 0 and 1. A value of 0 means exact matching of the search query.
expandThreshold (default: 50): When the user expands a node with too many neighbors, Linkurious Enterprise will ask to refine the query so that fewer neighbors are returned.
rawQueryLimit (default: 500): The maximum number of results returned by Linkurious Enterprise when executing a query or query template.
sampledItemsPerType (default: 1000): The number of nodes/edges per category/type to read from the graph for the schema sampling
sampledVisualizationItems (default: 1000): Number of nodes/edges to read from existing visualizations for the schema sampling
showBuiltinQueries (default: true): Whether built-in queries like Shortest Path should appear in the list of Graph Query templates.
slowQueryThreshold: (default: 500): Milliseconds after which a query is logged in the log file as a slow query.
extraCertificateAuthorities: Path to a PEM file. When set, the well known "root" CAs
(like LetsEncrypt) will be extended with the extra certificates in the
file. The file should consist of one or more trusted certificates in the PEM format.If Linkurious Enterprise is installed as a service, the service needs to be uninstalled and re-installed for the change to be taken into account.
obfuscation (default: false): Set to true if you want all the passwords in the configuration to be obfuscated at the next restart of Linkurious Enterprise.Linkurious Enterprise allows you to search your graph using natural full-text search.
In order to offer the search feature out-of-the-box, Linkurious Enterprise ships with an embedded Elasticsearch server. This option allow for zero-configuration deployment in many cases.
By default, Linkurious Enterprise uses Elasticsearch for search. This options requires Linkurious Enterprise to index your graph database, which technically means that Linkurious Enterprise will feed the whole content of the graph database to Elasticsearch to make it searchable. The time required to index the graph database increases with the size of the graph and this solution has limits in its scalability.
Indexation typically happens at speeds between 2000 and 20000 nodes or edges per second, depending on the number of properties for nodes and edges, and hardware performances.
By default, Linkurious Enterprise ships with an embedded Elasticsearch server (version 1.4.5).
This server only listens for local connections on a non-default port (it binds to 127.0.0.1:9201),
for security reasons and to avoid collisions with existing servers.
It is possible to use your own Elasticsearch cluster for performances reasons. Linkurious Enterprise supports Elasticsearch v1.x and v2.x. See details about Elasticsearch configuration options.
Using Elasticsearch is convenient but may not fit cases where the graph database is big (more than a couple million nodes and edges) and is regularly modified from outside Linkurious Enterprise, which required to re-index the whole database.
In order to offer a scalable search feature on big graphs, Linkurious Enterprise offers alternatives search solution. See details about the different options.
You can configure your search engines via the Web user interface
or directly on the linkurious/data/config/production.json file.
Using an administrator account, access the Admin > Data menu to edit the current data-source configuration:
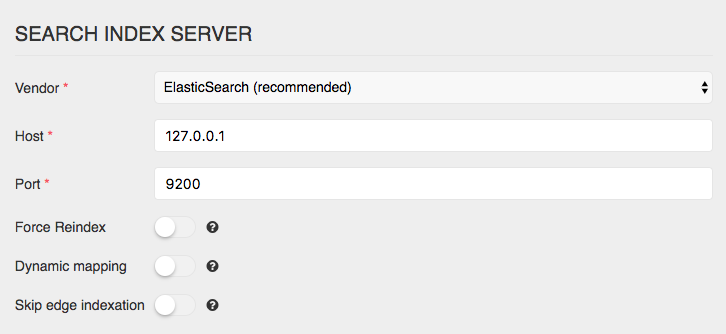
Edit the search engine configuration to connect to your graph database:
Submit the changes by hitting the Save configuration button.
Edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
See details for each supported search connector.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Onboarding | Does this search option require additional configuration, or can it be used out-of-the-box with the associated graph database? |
| Fast indexation | How fast is indexation? Note that this is a relative metric; while some search options may be faster than others, speed will depend on the complexity of your data model and your hardware limitations. |
| Automatic index sync | Are changes made to the graph DB propagated to the index automatically? |
| Search scalability | How well search queries perform for large graph databases? The actual upper limit on the performance of a given option will vary from vendor to vendor. |
| Advanced search | If advanced search features are available, such as numerical and date range search operators. |
| Onboarding | Fast indexation | Automatic index sync | Search scalability | Advanced search | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embedded Elasticsearch | Plug-and-play | No | No | Won't scale beyond ~100M nodes | Yes (requires configuration) |
| External Elasticsearch (v2+) | Requires Elasticsearch installation and configuration | No | No | Yes (by adding hardware to Elasticsearch cluster) | Yes (requires configuration) |
| Neo4j-to-Elasticsearch | Requires Elasticsearch installation and configuration + Neo4j plugin installation and configuration | Yes (up to 10,000 nodes/second) | Yes | Yes (by adding hardware to Elasticsearch cluster) | Yes |
| Neo4j Search (v3.5.1+) | Requires configuration in Neo4j (properties to index must be specified) | Yes | Yes | Limited | No |
| Onboarding | Fast indexation | Automatic index sync | Search scalability | Advanced search | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embedded Elasticsearch | Plug-and-play | No | No | Won't scale beyond ~100M nodes | Yes (requires configuration) |
| External Elasticsearch (v2+) | Requires Elasticsearch installation and configuration | No | No | Yes (by adding hardware to Elasticsearch cluster) | Yes (requires configuration) |
| Onboarding | Fast indexation | Automatic index sync | Search scalability | Advanced search | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Embedded Elasticsearch | Plug-and-play | No | No | Won't scale beyond ~100M nodes | Yes (requires configuration) |
| External Elasticsearch (v2+) | Requires Elasticsearch installation and configuration | No | No | Yes (by adding hardware to Elasticsearch cluster) | Yes (requires configuration) |
| Onboarding | Fast indexation | Automatic index sync | Search scalability | Advanced search | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AzureSearch | Requires AzureSearch setup (easy) | Yes | Yes | Yes | No |
| Embedded Elasticsearch | Plug-and-play | No | No | Won't scale beyond ~1M nodes | Yes (requires configuration) |
| External Elasticsearch (v2+) | Requires Elasticsearch installation and configuration | No | No | Won't scale beyond ~1M nodes | Yes (requires configuration) |
The neo4jSearch connector is a solution for full-text search with Neo4j.
neo4jSearch is supported since version 3.5.1 of Neo4j.
Linkurious can use the builtin search indices managed by Neo4j itself.
You can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json to set the index.vendor property to the value neo4jSearch.
To edit the Neo4j data-source configuration,
you can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474/" "user": "myNeo4jUser" "password": "nyNeo4jPassword" "index": "vendor": "neo4jSearch" "indexEdges": true Supported index options with Neo4jSearch:
indexEdges (optional): Whether to create or use an edge indexNote that, in Neo4jSearch, only fields stored in Neo4j as string will be searchable. Numerical and date properties won't be searchable if stored in Neo4j as numbers or native dates.
Neo4j-to-elasticsearch is a Neo4j plugin that enables automatic synchronization between Neo4j and Elasticsearch. This means that all changes to Neo4j are automatically propagated to Elasticsearch.
Neo4j-to-elasticsearch plugin is not compatible with Neo4j v4.x.
Follow these steps to install the plugin:
A.B.C.x where A.B.C matches your Neo4j version and x is 44 or laterA.B.C.x.y where A.B.C matches your Neo4j version and x.y is 44.8 or latergraphaware-server-community-all-A.B.C.x.jar and graphaware-neo4j-to-elasticsearch-A.B.C.x.y.jar to your neo4j/plugins directoryneo4j/conf/neo4j.conf):com.graphaware.runtime.enabled=truecom.graphaware.module.ES.1=com.graphaware.module.es.ElasticSearchModuleBootstrappercom.graphaware.module.ES.uri=HOST_OF_YOUR_ELASTICSEARCH_SERVERcom.graphaware.module.ES.port=PORT_OF_YOUR_ELASTICSEARCH_SERVERcom.graphaware.module.ES.mapping=AdvancedMappingcom.graphaware.module.ES.keyProperty=com.graphaware.module.ES.retryOnError=truecom.graphaware.module.ES.asyncIndexation=truecom.graphaware.module.ES.initializeUntil=2000000000000 # Set "relationship" to "(false)" to disable relationship (edge) indexation. # Disabling relationship indexation is recommended if you have a lot of relationships and don't need to search them. com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship= com.graphaware.runtime.stats.disabled=truecom.graphaware.server.stats.disabled=trueneo4j/conf/neo4j.conf:com.graphaware.module.ES.initializeUntil=2000000000000Please note that indexation could fail if your data uses different data types for the same property key. For example, if a property representing a date uses ISO strings in some nodes and timestamps in others. If you encounter this issue, please get in touch.
initializeUntilThe initializeUntil specification is used to trigger the indexation of existing Neo4j data in Elasticsearch. This is because com.graphaware.module.ES.initializeUntil must
be set to a number slightly higher than a Java call to System.currentTimeInMillis() would normally return
when the module is started. Thus, the database will be (re-)indexed only once, and not with every subsequent restart.
In other words, re-indexing will happen if
System.currentTimeInMillis() < com.graphaware.module.ES.initializeUntil.
Once the neo4j-to-elasticsearch plugin is installed, you need to change
the relevant data-source configuration to use neo2es as its search index vendor.
You can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json to set the index.vendor property to the value neo2es.
For smaller indexation tasks, neo4j-to-elasticsearch can be used straight out of the box. Larger indexes are trickier. If you find that indexation is failing to complete, or that search is unusually slow, you will need to settle for partial indexation in order to keep Elasticsearch usable.
Partial indexation can be configured in your Neo4j configuration file (neo4j/conf/neo4j.conf) by specifying a subset of your graph to index. You can do this by selecting which types of nodes and relationships to keep and which properties to index on these nodes.
(For a detailed list of configuration options, please consult Neo4j-to-elasticsearch's official documentation, available at Graphaware's Github repo. This guide will focus on a few use cases that should be adaptable to a wide variety of graph models.)
Partial indexation is handled by four options which can be added to your Neo4j configuration file:
com.graphaware.module.ES.node=...com.graphaware.module.ES.node.property=...com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship=...com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship.property=...com.graphaware.module.ES.node and com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship control which nodes and relationships to index. com.graphaware.module.ES.node.property and com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship.property control which properties of these nodes and relationships to index.
Each of these lines is followed by one or more parameters. Parameters are boolean expressions. They can be chained together using standard logical operators && (AND) and || (OR). The most basic parameters are (true) and (false). They will tell Elasticsearch either to index everything (the default behavior) or to index nothing. Note that the parentheses are required in order to force Elasticsearch to ignore these nodes while loading your database into the index.
To reiterate, if we add the line
com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship=(false)to our configuration file, Elasticsearch will not index any of the relationships in our database.
The next step up is parameter functions. These allow for more complex inclusion and exclusion rules. For both nodes and relationships, the following two functions are available:
getProperty('propName', 'defaultValue'): Returns a property value, allowing you to compare it to another value using standard comparison operators.hasProperty('propName'): Returns true or false depending on whether a node or relationship contains a certain property.Additionally, there are functions specific to nodes and to relationships. For nodes, those that are useful for partial indexation are:
getDegree(): Returns the degree (number of relationships) of a node. Can be used with comparison operators.hasLabel('labelName'): Returns true or false depending on whether the specified label is present on a node.And for relationships, they are:
isType('typeName'): Returns true or false depending on whether the specified type is present on a relationship.isOutgoing(): Returns true or false depending on whether a relationship is outgoing.isIncoming(): Returns true or false depending on whether a relationship is incoming.(You can find a full list of functions in Graphaware's inclusion policies maintained on their Github repo.)
Say we have a due diligence database containing people, banks, account numbers, addresses, telephone numbers, and email addresses. It's a large database -- several hundred million nodes -- so to fully index the graph would be a lengthy process, and may ultimately be unnecessary if we are only interesting in full-text search on a restricted set of node and relationship properties.
The first question we should ask is about this data we are interested in. Maybe as part of our hypothesis about the data, we want to focus on a certain subset of connections that we believe form patterns of interest.
Let's say that we want to focus on identifying information only -- we think that there are cases where this information is shared by multiple individuals, for instance, and we're interested in analyzing them. The nodes of interest to us will therefore be those nodes which represent pure identifiers and not entities themselves -- addresses, telephone numbers, account numbers, and email addresses. We can tell Elasticsearch to index these and only these by adding the following line to our Neo4j configuration file:
com.graphaware.module.ES.node=hasLabel('Address') || hasLabel('Telephone') || hasLabel('Email') || hasLabel('Account')(com.graphaware.module.ES.node=!hasLabel('Person') && !hasLabel('Bank') will also work.)
And since we aren't including people or banks, we also want to focus on the relationships relevant to our nodes of interest:
com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship=isType('HAS_ADDRESS') || isType('HAS_PHONE') || isType('HAS_EMAIL') || isType('HAS_ACCOUNT')If we want to be even more specific, we can select only those properties which are relevant to our inquiry by adding com.graphaware.module.ES.node.property to our config. We follow this with a list of keys, or node property names, (separated by || (OR) statements) that we want to include in our index:
com.graphaware.module.ES.node.property=key == 'address1' || key == 'city' || key == 'state' || key == 'number' || key == 'email' || key == 'accountNumber'And if we only want to index nodes and NOT relationships, we can disable relationship indexation completely:
com.graphaware.module.ES.relationship=(false)Since relationships are often more numerous than nodes, excluding them from our index can significantly reduce its storage footprint.
What if we finish our initial analysis and conclude that we need to know more about the financial institutions in our graph? We want to add banks to our index, but we don't need to search everything that is stored on them. Furthermore, we're only interested in banks in a certain region -- Europe, say. We can add the right banks back by modifying our original directive to read:
com.graphaware.module.ES.node=hasLabel('Address') || hasLabel('Telephone') || hasLabel('Email') || hasLabel('Account') || (hasLabel('Bank') && getProperty('bankRegion', 'None') == 'Europe')And we can add a few bank properties like this:
com.graphaware.module.ES.node.property=key == 'address1' || key == 'city' || key == 'state' || key == 'number' || key == 'email' || key == 'accountNumber' || key == 'bankName' || key == 'bankIdentifier' || key == 'bankRegion'Keep in mind that these keys will be indexed for every node on which they appear. If banks have a state property, for example, it will be added to the index for state. It's worth remembering this when constructing your data model. Namespace collisions can prove computationally costly.
Neo4j-to-Elasticsearch, in combination with partial indexation strategies, can be a very efficient way of handling index synchronization for large graphs. Even if your graph is small enough to index in full, it's worth considering to what extent it may grow. By examining your problem space and choosing only a subset of the information available to you for your traversal needs, you may save yourself future headaches and maximize the efficiency of your graph.
Azure search is the recommended full text search solution for Cosmos DB.
Linkurious requires an index on nodes to perform a search. If you do not have a configured index yet, you can create one via the azure portal.
Additionally, you can create an index on edges if you want search them as well with Linkurious.
Please review the description of each index attributes and make sure the label field is marked
as filterable. Linkurious will not be able to use the index otherwise.
To edit the AzureSearch data-source configuration,
you can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graphdb": "vendor": "cosmosDb" "url": "https://your-service.gremlin.cosmosdb.azure.com:443/" "database": "your-graph-database" "collection": "your-collection" "primaryKey": "your-account-primary-key" "index": "vendor": "azureSearch" "url": "https://your-search-service.search.windows.net" "apiKey": "your-search-service-admin-api-key" "nodeIndexName": "your-node-index-name" "edgeIndexName": "your-edge-index-name" Supported index options with Azure search:
url (required): URL of the search serviceapiKey (required): Primary Admin Key of the search servicenodeIndexName (required): Name of the node index of your graph databaseedgeIndexName (optional): Name of the edge index of your graph databasePlease refer to the Azure search online documentation for details on how to load data into Azure search.
Note that today, in Azure Search, it's not possible to search on numbers or dates. If you are interested in this feature, please get in touch.
Elasticsearch is supported from version 1.4.0 (using the elasticSearch connector)
and for version 2.x and version 6.x (using the elasticSearch2 connector).
Elasticsearch 7 is not yet supported in Linkurious Enterprise 2.9.14.
Linkurious Enterprise ships with an embedded Elasticsearch server (version 1.4.5).
ATTENTION: The internal Elasticsearch is not intended to be used for graph databases > 50,000,000 nodes. Though indexation and search performance are ultimately dependent on hardware limitations, it has been configured to prevent horizontal scaling and so is not an efficient choice for large DBs. It is meant instead as a quick indexation strategy for POCs or small deployments.
To use the Linkurious Enterprise embedded Elasticsearch instance, set the following index configurations keys:
vendor must be elasticSearchhost must be "127.0.0.1"port must be 9201Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graph": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474" "index": "vendor": "elasticSearch" "host": "127.0.0.1" "port": 9201 Search connector elasticSearch supports the following options:
host (required): Elasticsearch server hostport (required): Elasticsearch server port (standard is 9200)https: true to connect to Elasticsearch via HTTPSuser: Elasticsearch username (if you are using X-Pack Security, a.k.a ElasticShield)password: Elasticsearch passwordforceReindex: true to re-index the data-source each time Linkurious Enterprise startsskipEdgeIndexation: true to skip edges indexation (edges won't be searchable)analyzer (default: "standard"): The custom analyzer aimed at analyzing a specific language text. (see available language analysers)dynamicMapping: true to enable number parsing for advanced number search features (range, etc.)Example configuration:
"dataSources": "graph": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474" "index": "vendor": "elasticSearch" "host": "192.168.1.80" "port": 9200 "dynamicMapping": false Search connector elasticSearch2 supports the following options:
host (required): Elasticsearch server hostport (required): Elasticsearch server port (standard is 9200)https: true to connect to Elasticsearch via HTTPSuser: Elasticsearch username (if you are using X-Pack Security, a.k.a ElasticShield)password: Elasticsearch passwordforceReindex: true to re-index the data-source each time Linkurious Enterprise startsskipEdgeIndexation: true to skip edges indexation (edges won't be searchable)analyzer (default: "standard"): The custom analyzer aimed at analyzing a specific language text. (see available language analysers)dynamicMapping: true to enable number parsing for advanced number search features (range, etc.)forceStringMapping: List of fields that are mapped to strings even with dynamicMapping is truecaCert: Absolute path to a Certificate Authority certificate in PEM formatExample configuration:
"dataSources": "graph": "vendor": "neo4j" "url": "http://127.0.0.1:7474" "index": "vendor": "elasticSearch2" "host": "192.168.1.122" "port": 9200 "skipEdgeIndexation": true To enable search on numerical and date properties is necessary to set to true the option dynamicMapping described above.
It's also necessary to declare correctly these properties as numbers or dates in the Linkurious Enterprise schema.
Note that, today, only date properties stored in Neo4j as ISO dates are currently searchable.
If you have issue configuring search on numerical or date properties, please get in touch.
By default, Linkurious Enterprise ships with an embedded Elasticsearch instance which works out-of-the-box by default. The embedded Elasticsearch instance will work well for average to large database sizes, but for search-heavy use-cases or very large databases, configuring your own Elasticsearch cluster might be necessary.
An easy way to deploy an easy-to-scale Elasticsearch cluster yourself is to use Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Please follow these steps to create a configure your AWS Elasticsearch cluster with Linkurious Enterprise:
Visit the Amazon Web Services website and create your account (or log in if you already have one).
Visit the Amazon Elasticsearch Service page, log-in and follow the steps to create an Elasticsearch cluster:
Select Services > Elasticsearch Service
Click get started

Name your cluster (1) and select the Elasticsearch version 2.x (2), click Next
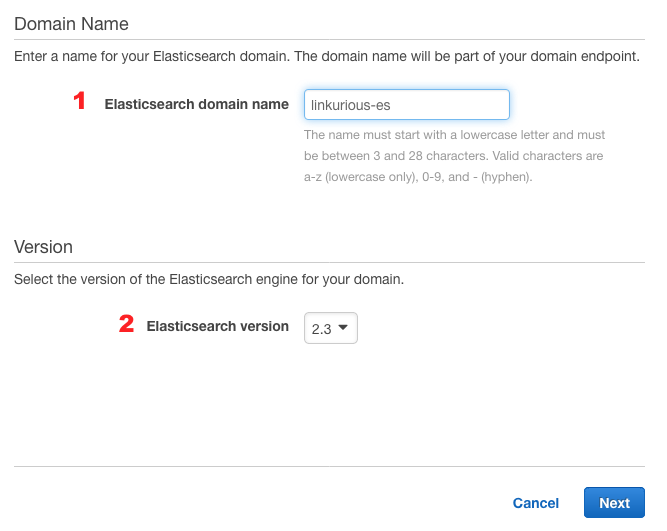
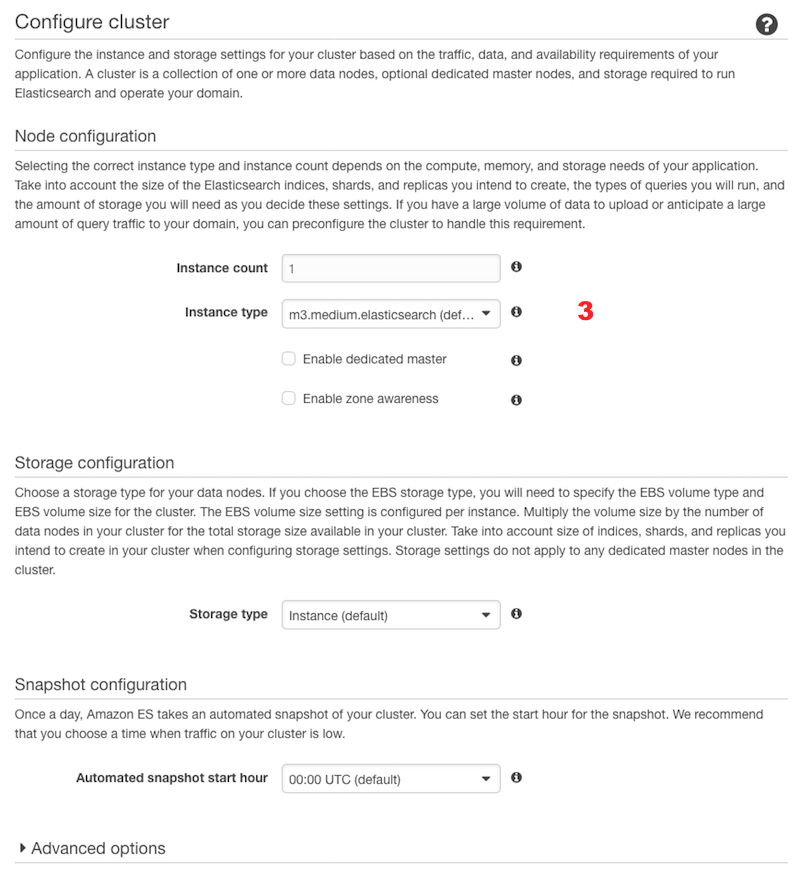
Select the instance type, the number of instances and the number of dedicated masters in your cluster (3), depending on your database's size
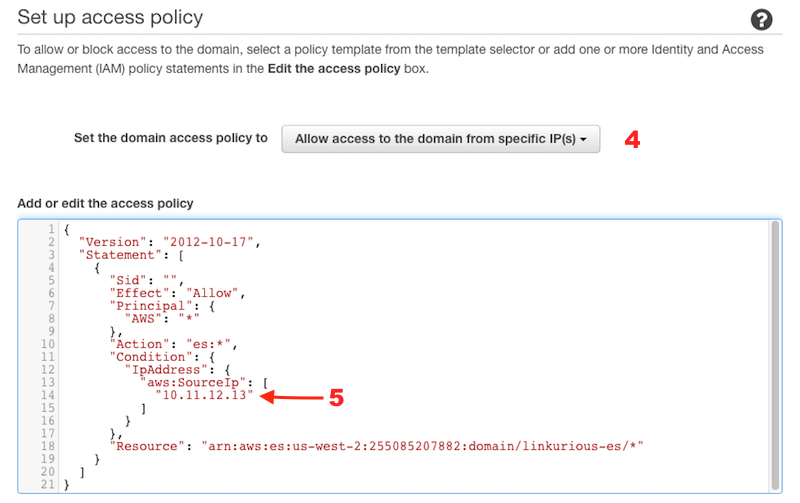
Configure the access policy for your cluster. Use access from specific IP (4) and enter the public IP address of your Linkurious Enterprise server (5)
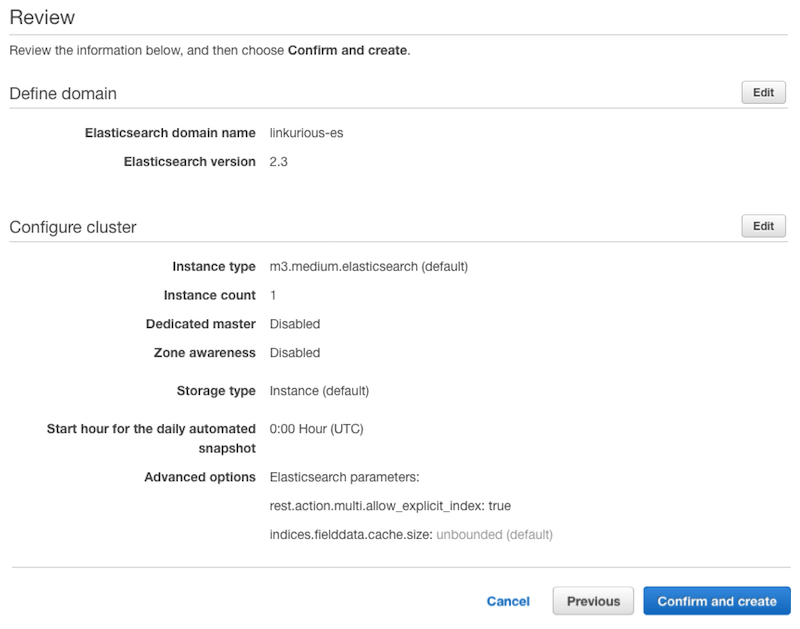
Review your configuration and confirm the creation of the cluster
Wait until the cluster is deployed (usually less than an hour)
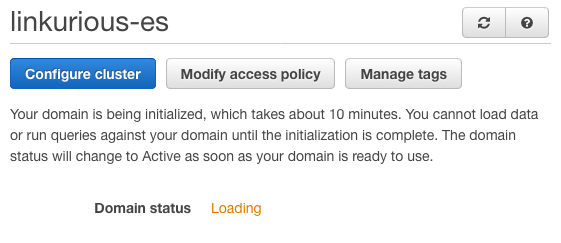
When your cluster is deployed, copy the Endpoint host name
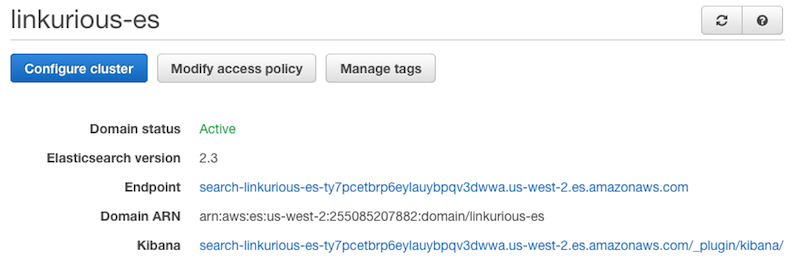
Configure Elasticsearch as explained here
Linkurious Enterprise uses an SQL database to store user-data. The database contains:
By default, the user-data store is a SQLite file-based database. This makes Linkurious Enterprise easy to deploy.
For deployment at scale (more than a couple users), we recommend switching to one of the supported server-based databases:
MySQL 8 is not yet supported in Linkurious Enterprise 2.9.14.
SQLite if the default user-data store of Linkurious Enterprise.
"db": "name": "linkurious" "options": "dialect": "sqlite" "storage": "server/database.sqlite" "db": "name": "linkurious" "username": "MYSQL_USER_NAME" "password": "MYSQL_PASSWORD" "options": "dialect": "mysql" "host": "MYSQL_HOST" "port": 3306 "db": "name": "linkurious" "username": "MSSQL_USER_NAME" "password": "MSSQL_PASSWORD" "options": "dialect": "mssql" "host": "MSSQL_HOST" "port": 1433 "db": "name": "linkurious" "username": "MARIADB_USER_NAME" "password": "MARIADB_PASSWORD" "options": "dialect": "mariadb" "host": "MARIADB_HOST" "port": 3306 The default storage system for Linkurious Enterprise is SQLite.
Configuring Linkurious Enterprise to work with MySQL is a really easy procedure if you don't need to migrate data from SQLite.
Migrating data from SQLite to an external database is possible but it is a procedure we would recommend only if restarting from scratch with the new configuration is not a viable option.
Our public resources contain a specific tool needed to perform the migration from SQLite to one of the supported databases, as well as the detailed list of steps to use and eventually configure the tool.
If you need help with the procedure please contact us at support@linkurio.us.
If you are using the SQLite database (by default), you only need to follow the standard Linkurious Enterprise backup procedure.
If you are using another database to store the Linkurious Enterprise user-data, please refer to one of the following guides:
The web server of Linkurious Enterprise delivers the application to end users through HTTP/S.
It is configured in the server configuration key within the configuration
file (linkurious/data/config/production.json):
Within the server key:
listenPort (default: 3000): The port of the web serverSome firewalls block network traffic ports other than 80 (HTTP).
Since only root users can listen on ports lower than 1024,
you may want reroute traffic from 80 to 3000 as follows:
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 80 -j REDIRECT --to-port 3000If you use SSL, you can add a second rule to redirect 3443 to 443:
sudo iptables -t nat -A PREROUTING -p tcp --dport 443 -j REDIRECT --to-port 3443Within the server key:
baseFolder (default: /): The base path where Linkurious Enterprise will be foundIn some cases, you may want to host Linkurious Enterprise on a path other than root for a particular domain.
For example, if you want Linkurious Enterprise to be reachable at http(s)://HOST:PORT/linkurious you should
set baseFolder equal to linkurious.
Within the server key:
domain (default: "localhost"): The domain or sub-domain used to access the web server.
It is mandatory to edit it for publishing visualizations online.
It is also used to restrict the validity of cookies to a domain or sub-domain.publicPortHttp (default: listenPort): The public HTTP port of the web server.publicPortHttps (default: listenPortHttps): The public HTTPS port of the web server.In some cases, Linkurious Enterprise needs to generate links to itself (for example when generating a link to a widget). For that, the server needs to know its public domain and port to generate those links.
The public port can be different from the actual port if you use traffic rerouting
(using a firewall or a reverse-proxy). In the example above (traffic rerouting),
the actual HTTP port (listenPort) is 3000, but the public HTTP port (publicPortHttp)
is 80.
Within the server key:
cookieSecret (optional): Set the secret used to compute the hash of you session.cookieDomain (optional): Set this value if you need your cookie to be set for a domain different from domain.cookieHttpOnly (default: true): Set the httpOnly flag of your cookies.cookieSecure (default: false): Set the secure flag of your cookies.Within the server key:
allowOrigin (default: "*"): Define the cross-origin resource sharing (CORS) policy.
Accept cross-site HTTP/S requests by default. The value can be:
"abc.com"): only requests from "abc.com" domain are allowed."*.abc.com"): request from all sub-domains of abc.com are allowed.["abc.com", "*.def.com"]): requests from abc.com and all sub-domains of def.com are allowed."*"): requests from any domain are allowed.Within the server key:
allowFraming (default: false): Whether a browser should render Linkurious inside a frame.By default, Linkurious doesn't allow framing by returning at each request the following HTTP header:
X-Frame-Options:SAMEORIGIN.
Setting the configuration key to true will remove the X-Frame-Options HTTP header.
Within the server key:
customHTTPHeaders (optional): For compliance, custom HTTP headers can be added to configuration to be returned
in the headers with each response from the server.Example:
customHTTPHeaders:'header1': 'value1''header2': 'value2'...
Note: Some header keys are reserved for LKE and will be overwritten by the server to default values.
Within the ogma.settings.render key:
imgCrossOrigin (default: "anonymous"): Restrict the origin of images
displayed in visualizations to prevent running malicious code on the graphic card of users.
Display images from any origin by default. Read here to learn more.Within the server key:
listenPortHttps (default: 3443): The port of the web server if HTTPS is enabled. See the Install section to learn why you should not set 443 directly.useHttps (default: false): Encrypt communications through HTTPS if true. Requires a valid SSL certificate.forceHttps (default: false): Force all traffic to use HTTPS only if true.forcePublicHttps (default: false): Force all generated URL in Linkurious Enterprise to use HTTPS (useful when HTTPS is not enabled in Linkurious Enterprise but offered by an external reverse proxy).
The server will redirect HTTP GET requests to HTTPS and reject all other HTTP requests.certificateFile: The relative path to the SSL certificate (must be in PEM format, located within the linkurious/data folder).certificateKeyFile: The relative path to a private key of the SSL certificate (must be in PEM format, located within the linkurious/data folder).certificatePassphrase: The pass-phrase protecting the SSL certificate (if any).tlsCipherList (optional): The ciphers supported by any connection established by Linkurious Enterprise as a server or client. It expects a string in OpenSSL cipher list format. The default value is tls.DEFAULT_CIPHERS.External communications with the Linkurious Enterprise server can be secured using SSL without installing third-party software.
If the Linkurious Enterprise server, graph database, and the search index are installed on different machines, we recommend using secure communication channels between these machines (e.g. HTTPS or WSS). Please refer to the data-source documentation and search index documentation to learn how to enable HTTPS.
To use custom Certificate Authorities (CA), please check how to use additional Certificate Authorities in Linkurious Enterprise.
The TLS protocols supported by Linkurious Enterprise server are TLSv1.0, TLSv1.1 and TLSv1.2. If for compliance reasons you want to manually disable TLSv1.0 and TLSv1.1, you can open the file
data/manager/manager.jsonand add"--tls-min-v1.2",above"server/app.js",, save the file and restart Linkurious Enterprise.
By default, user authentication is disabled and all actions are
performed under the special account named Unique User.
The unique user has unrestricted access and does not require a password, so anyone can access the platform.
We strongly advise you to enable user authentication to secure the access to your data once Linkurious Enterprise is deployed on a server.
There are 2 possible authentication options:
Local authentication can be enabled from Linkurious Enterprise user interface.
Once local authentication is enabled, users need an account to access Linkurious Enterprise. Administrators can create accounts directly in Linkurious Enterprise (see how to create users).
To enable authentication use the Web user interface via the Admin > Users menu:
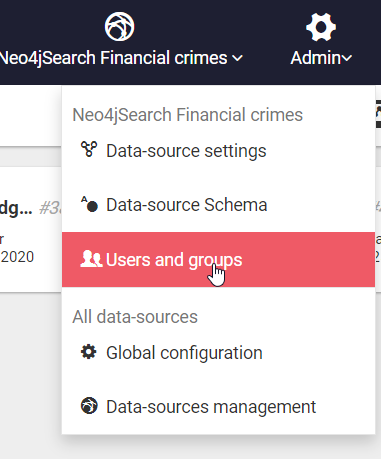
The following screen will be prompted if authentication is disabled. Click Enable Authentication.
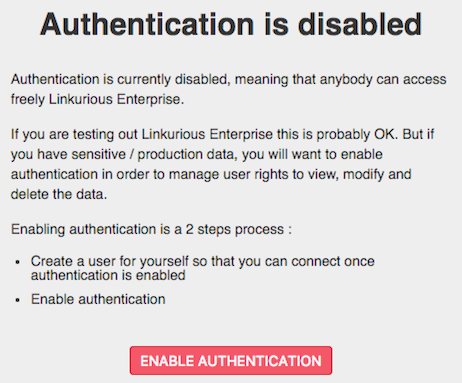
Create an admin account and click Save and enable.
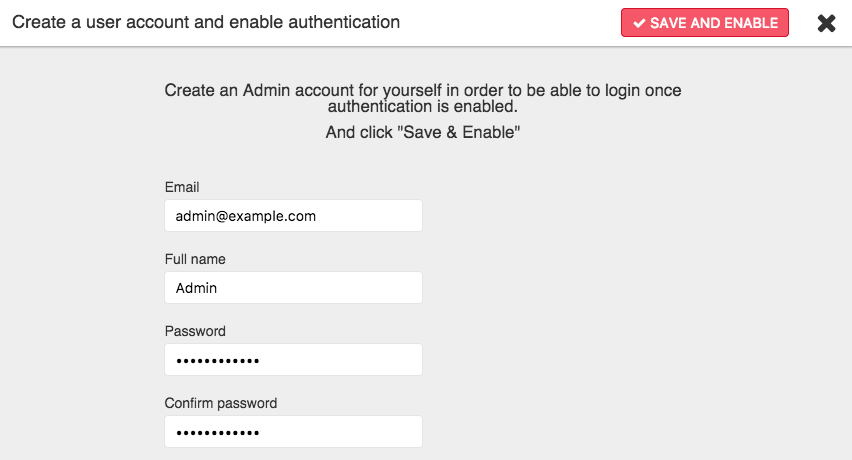
Passwords of local users are hashed with the PBKDF2 algorithm and the following parameters:
When using an external source for authentication, users are automatically created in Linkurious Enterprise when they connect for the first time.
These shadow-users allow to store specific data such as preferences, groups and visualizations.
Passwords of external users are never stored inside Linkurious Enterprise.
Linkurious Enterprise supports the following external authentication services:
If your company uses an authentication service that Linkurious Enterprise does not support yet, please get in touch.
If you enable an Single-Single-On (SSO) capable authentication service (OAuth/OpenID Connect or SAML2), your users won't need to login directly in Linkurious Enterprise but, instead, by clicking the SSO button they will be redirected to the identity provider for authentication.

If an external source already organizes users in groups, it's possible to use this information to map automatically
external groups to Linkurious groups. To do so, you have to set the access.externalUsersGroupMapping configuration key
to be an object with the external group IDs as keys and the internal group IDs as values.
For example, if we want to provide group mapping for Microsoft Active Directory:
// under the access configuration key // ... "externalUsersGroupMapping": "Administrators": 1 // any Active Directory admin is a Linkurious admin // ... For some identity providers the external group IDs is an actual name, for others is an ID:
"818b6e03-15dd-4e19-8cb1-a4f434b40a04"access.ldap.groupField"Administrators" or the group distinguished name, e.g. "CN=Administrators,CN=Users,DC=linkurious,DC=local"To exclude some groups of users from logging in into Linkurious, set up a list of
authorized groups in the configuration key access.externalUsersAllowedGroups.
// under the access configuration key // ... "externalUsersAllowedGroups": "CN=Administrators,CN=Users,DC=linkurious,DC=local" "CN=Analysts,CN=Users,DC=linkurious,DC=local" // ... By default, when an external user is connected for the first time, their external groups are mapped once.
So any change in the user's group in the external source would not be reflected in the LKE user.
However, setting autoRefreshGroupMapping to true makes an external user's groups
to be reset according to externalUsersGroupMapping, each time the external user logs in.
// under the access configuration key // ... "autoRefreshGroupMapping": true // ... Also, note that when autoRefreshGroupMapping is true updating external users' groups from within LKE is not allowed.
If Linkurious Enterprise is connected to an LDAP service, users will be authenticated using the external service at each log-in.
If you have a LDAP service running in your network, you can use it to authenticate users in Linkurious Enterprise.
Contact your network administrator to ensure that the machine where Linkurious Enterprise is installed can connect to the LDAP service.
For OpenLDAP compatible providers, add or edit the existing ldap section inside the access configuration.
Allowed options in access.ldap:
enabled: true to enable this authentication strategyurl: URL of the LDAP serverbindDN (optional): "Domain Name" of the LDAP account used to search other accountsbindPassword (optional): Password of the LDAP account used to search other accountsbaseDN: Base "Domain Name" in which users will be searched. It can be a string or a non-empty array of stringsusernameField: Name of the LDAP attribute containing the user's nameemailField: Name of the LDAP attribute containing the user's e-mailgroupField (optional): Name of the LDAP attribute containing the user's groupThe bindDN and bindPassword are optional. If specified they will be used to bind to the LDAP server.
Example LDAP configuration:
"access": // [...] "ldap": "enabled": true "url": "ldap://ldap.forumsys.com:389" "bindDN": "cn=read-only-admin,dc=example,dc=com" "bindPassword": "password" "baseDN": "dc=example,dc=com" "usernameField": "uid" "emailField": "mail" "groupField": "group" For Microsoft Active Directory, add a msActiveDirectory section inside the access configuration.
Allowed options in access.msActiveDirectory:
enabled: true to enable this authentication strategyurl: URL of the Active Directory serverbaseDN: Base "Domain Name" in which users will be searcheddomain: (optional) Domain of your Active Directory servernetbiosDomain: (optional) NetBIOS domain of your Active Directory servertls.rejectUnauthorized: (optional) Whether the SSL certificate of your Active Directory server will be checkedUsers can authenticate with their userPrincipalName or their sAMAccountName.
Use the domain configuration key to avoid your users to specify the domain part of their userPrincipalName.
Use the netbiosDomain configuration key to avoid your users to specify the NetBIOS domain part of their sAMAccountName.
Example Active Directory configuration:
"access": // [...] "msActiveDirectory": "enabled": true "url": "ldaps://ldap.lks.com:636" "baseDN": "dc=ldap,dc=lks,dc=com" "domain": "ldap.lks.com" "netbiosDomain": "LINKURIO" "tls": "rejectUnauthorized": true In alternative is possible to use your on premises Active Directory in conjunction with Azure Active Directory to provide SSO to your users. Please refer to Prerequisites for Azure AD Connect for more information and to SSO with Azure AD to know how to setup Azure AD as an identity provider.
Linkurious Enterprise supports Microsoft Azure Active Directory as an external authentication provider.
To set up Linkurious Enterprise authentication with Microsoft Azure Active Directory, follow these steps:
Linkurious in Azure Active Directory on Azure PortalDirectory.Read.All access right to the new app (notice: an Azure admin's approval is needed)authorizationURL, e.g. https://login.microsoftonline.com/60d78xxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx9ca39b/oauth2/authorizetokenURL, e.g. https://login.microsoftonline.com/60d78xxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx9ca39b/oauth2/tokenclientID, e.g. 91d426e2-xxx-xxxx-xxxx-989f89b6b2a2clientSecret, e.g. gt7BHSnoIffbxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxtyAG5xDotC8I=tenantID, (optional, required only for group mapping) e.g. 60d78xxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxx9ca39boauth2 section inside the access section in linkurious/data/config/production.jsonExample access.oauth2 configuration with Microsoft Azure Active Directory:
"access": // [...] "oauth2": "enabled": true "provider": "azure" "authorizationURL": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX/oauth2/authorize" "tokenURL": "https://login.microsoftonline.com/XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX/oauth2/token" "clientID": "XXXXXXXX-XXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX" "clientSecret": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" "azure": "tenantID": "XXXXXXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXX" The Oauth2 redirect URL of Linkurious Enterprise is the following:
http(s)://HOST:PORT/api/auth/sso/return.
Linkurious Enterprise supports Google Suite (a.k.a. Google Apps) as an external authentication provider (with Single Sign-On).
Since Google Suite implements the OpenID Connect standard, it can be configured as an OpenID Connect provider.
To set up Linkurious Enterprise authentication with Google Suite, follow these steps:
authorizationURL, e.g. https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/authtokenURL, e.g. https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/tokenclientID, e.g. 1718xxxxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.apps.googleusercontent.comclientSecret, e.g. E09dQxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxSNoauth2 section inside the access section in linkurious/data/config/production.jsonTo limit the access to the Google accounts from your Google Suite domain, use
the hd query parameter in the authorizationURL with your domain as value.
Example access.oauth2 configuration with Google Suite:
"access": // [...] "oauth2": "enabled": true "provider": "openidconnect" "authorizationURL": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth?hd=YOUR_GSUITE_DOMAIN.COM" "tokenURL": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token" "clientID": "XXXXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX.apps.googleusercontent.com" "clientSecret": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" Linkurious Enterprise supports any OpenID Connect compatible provider as external authentication providers.
OpenID Connect is an identity layer on top of the OAuth2 protocol. It allows applications (like Linkurious Enterprise) to verify the identity of End-User based on the authentication performed by an Authorization Server, as well as to obtain basic profile information about the End-User in an interoperable manner.
To set up Linkurious Enterprise authentication with an OpenID Connect provider, you need to obtain the following parameters from the provider:
authorizationURL, e.g. https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/authtokenURL, e.g. https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/tokenclientID, e.g. 1718xxxxxx-xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx.apps.googleusercontent.comclientSecret, e.g. E09dQxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxSNExample access.oauth2 configuration with any OpenID Connect provider:
"access": // [...] "oauth2": "enabled": true "provider": "openidconnect" "authorizationURL": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/v2/auth" "tokenURL": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v4/token" "clientID": "XXXXXXXXXX-XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX.apps.googleusercontent.com" "clientSecret": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" The Oauth2 redirect URL of Linkurious Enterprise is the following:
http(s)://HOST:PORT/api/auth/sso/return.
To set up group mapping in OpenID Connect is necessary to specify additional configuration keys:
openidconnect.userinfoURL, e.g. https://XXXXXXXXXX.oktapreview.com/oauth2/v1/userinfoopenidconnect.scope, e.g. openid profile email groupsopenidconnect.groupClaim, e.g. groupsFor example if you want to set up OIDC with Okta:
"access": // [...] "oauth2": "enabled": true "provider": "openidconnect" "authorizationURL": "https://XXXXXXXXXX.oktapreview.com/oauth2/v1/authorize" "tokenURL": "https://XXXXXXXXXX.oktapreview.com/oauth2/v1/token" "clientID": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" "clientSecret": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX" "openidconnect": "userinfoURL": "https://XXXXXXXXXX.oktapreview.com/oauth2/v1/userinfo" "scope": "openid profile email groups" "groupClaim": "groups" Linkurious Enterprise supports any SAML2 compatible provider as external authentication providers.
To set up Linkurious Enterprise authentication with a SAML2 provider, you need to obtain the following parameters from the provider:
url: The URL of the SAML2 endpoint of the identity provider (e.g."https://example.com/adfs/ls"`),identityProviderCertificate: The certificate of the identity provider in PEM format (e.g. "/Users/example/linkurious/samlIdentityProvider.pem")groupAttribute (optional): The attribute in which the groups of the users is stored (e.g. "Groups")emailAttribute (optional): The attribute in which the email of the users is storedgroupAttribute is the attribute of the SAML response containing the array of groups a user belongs to.
emailAttribute is the attribute of the SAML response that should contain the email address if the NameID format
of the SAML response is not already an email.
Example access.saml2 configuration with any SAML2 provider:
"access": // [...] "saml2": "enabled": true "url": "https://example.com/adfs/ls" "identityProviderCertificate": "/Users/example/linkurious/saml.pem" "groupAttribute": "Groups" To complete the login process, you need to configure your identity provider
to return the SAML response to Linkurious Enterprise at the following URL:
http(s)://HOST:PORT/api/auth/sso/return.
In particular, ADFS (Active Directory Federation Services) is a SAML2 provider that offers Single-Sign-On towards an Active Directory service, see more on Microsoft documentation.
To set up Linkurious Enterprise authentication with ADFS, Linkurious Enterprise has to be configured as a Relying Party Trust in ADFS (see how to configure the ADFS on the Microsoft documentation).
To set up group mapping, the list of groups associated to a user should be passed in the SAML2 response. See how to configure a claim for the groups on the Microsoft documentation.
The authentication is configured within the access configuration key
in the configuration file (linkurious/data/config/production.json):
authRequired (default: false): Whether to require authentication, see how to enable authentication.
guestMode (default: false): Enable the guest mode.
loginTimeout (default: Infinity): Seconds of inactivity after which a user is logged out.
dataEdition (default: true): Enable the creation, edition, and deletion of nodes and edges in all data-sources.
Permissions can be fine-tuned for each group, see the documentation about users and groups.
If set to false, all edition requests sent through Linkurious Enterprise to the data-sources will be rejected.
widget (default: true): Enable to publish visualizations online.
Published visualizations are always accessible by anonymous users.
externalUsersGroupMapping (optional): How to map external groups to Linkurious Enterprise groups
(see how to configure group mapping).
externalUsersAllowedGroups (optional): List of external groups of users allowed to log in into Linkurious Enterprise.
externalUserDefaultGroupId (optional): Default group id automatically set for new external users
when no other rule is set in externalUsersGroupMapping.
autoRefreshGroupMapping (default: false): If true, when an external user logs in, their groups are reset
according to externalUsersGroupMapping and are also not allowed to be updated.
ldap (optional): The connection to the LDAP service (see how to configure LDAP).
msActiveDirectory (optional): The connection to the Microsoft Active Directory service
(see how to configure Active Directory).
oauth2 (optional): The connection to an OAuth2/OpenID Connect identity provider
(see how to configure Azure AD, Google or a generic OpenID Connect provider).
saml2 (optional): The connection to a SAML2 identity provider (see how to configure SAML2 / ADFS).
floatingLicenses (default: Infinity): The maximum number of users that can connect to Linkurious Enterprise at the same time.
autoRefreshGroupMapping (default: false): If set to true access rights for an external user will be refreshed at every login
To access Linkurious Enterprise when authRequired is true, users need accounts in Linkurious Enterprise.
Administrators can create accounts directly in Linkurious Enterprise (see how to create users)
or rely on an external authentication service.
Linkurious Enterprise supports the following external authentication services:
If your company uses an authentication service that Linkurious Enterprise does not support yet, please get in touch.
If you enable an SSO capable authentication service (OAuth/OpenID Connect or SAML2), your users won't need to login directly in Linkurious Enterprise but, instead, by clicking the SSO button they will be redirected to the identity provider for authentication.
This page is accessed via Admin > Users & Groups in the main menu. The page lists all users, both local and external.
User management operations available to Administrators are the following:
In order to be able to access Linkurious Enterprise, users need to be assigned to at least 1 user group.
A user can be assigned to:
Group assignment can be done either while creating or editing a user account.
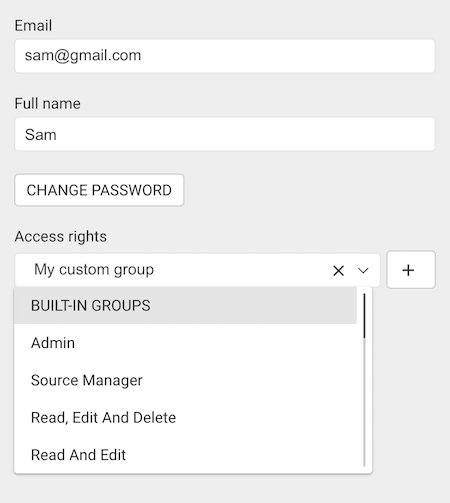
Linkurious Enterprise relies on a role-based access control model:
This page is accessed via Admin > Users & Groups in the main menu.
This page lists:
Group management operations available to the Administrators are the following:
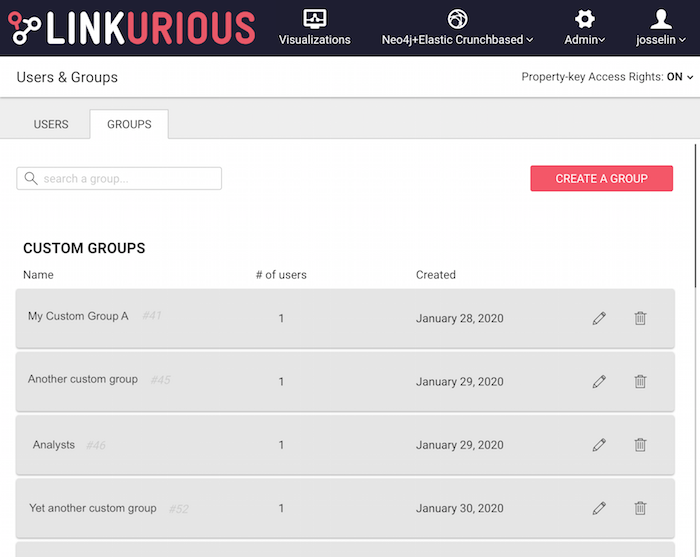
Creating a group is a 2-step process:
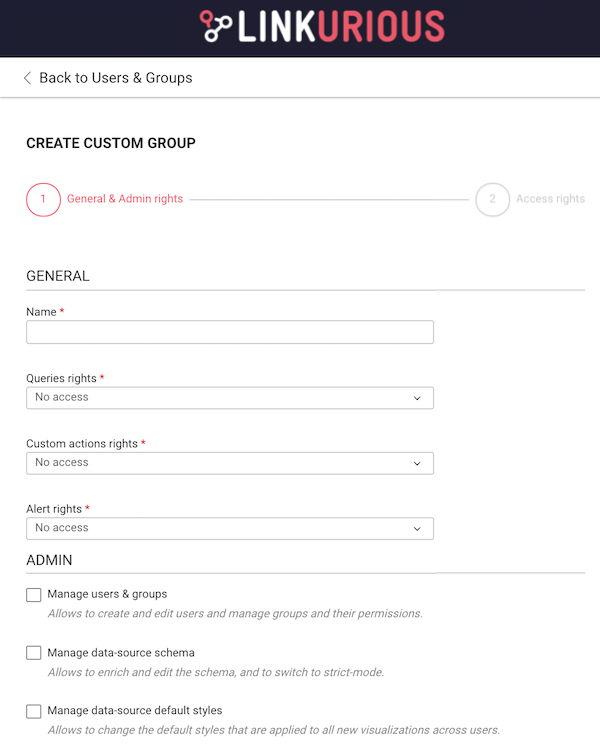
Queries access-rights
No access: the user group cannot execute queries (and cannot create them).Can run queries: the user group can execute read and write queries it was shared with, but cannot create them.Can create read-only queries and run queries:
Can create read/write queries and run queries:
Write queries are identified by keywords in their code:
- Cypher:
SET,CREATE,MERGE,DELETE,REMOVE,FOREACH,LOAD,DROP,CALL- Gremlin:
addProperty,property,addE,addV,drop,remove,clear
Custom actions access-rights
No access: the user group cannot execute custom actions (and cannot create them).Can run custom actions: the user group can execute custom action it was shared with but cannot create them.Can create and run custom actions:
Alert access-rights
No access: the user group cannot access the Alerts (and cannot create them).Process alerts: the user group can access the Alerts, process the matches but cannot create new Alerts.Create and process alerts: the user group can process existing Alerts and can create new Alerts.Admin access-rights
Manage users & groups: the user group can create and edit users and manage groups and their permissions.Manage data-source schema: the user group can enrich and edit the schema, and to switch to strict-mode.Manage data-source default styles: the user group can change the default styles that are applied to all new visualizations across users.Re-index the data-source: the user group can launch a re-index of the database. If handled without care, re-indexing might overload the database as indexing is a costly process.Re-connect the data-source: the user group can initiate a connection sequence when the connection has been interrupted.For users that belong to multiple groups, access-rights are cumulative. In other words, a user can do something if at least one of their groups allows them to do it.
For example if user belongs to 2 groups: one having No access and the
other Process Alerts for the Alert rights, then they have the right
to Process Alerts because one of their groups allows them to do so.
There are 2 available options. You can read about them in their dedicated sections:
NONE: The user can't access (search or display) nodes (resp. edges) of that category (rest. type).READ: The user can search display nodes (rest.edges) of that category (resp. type).EDIT: The user can edit properties of nodes (rest. edges) of that category (resp. type).CREATE AND DELETE: The user can:
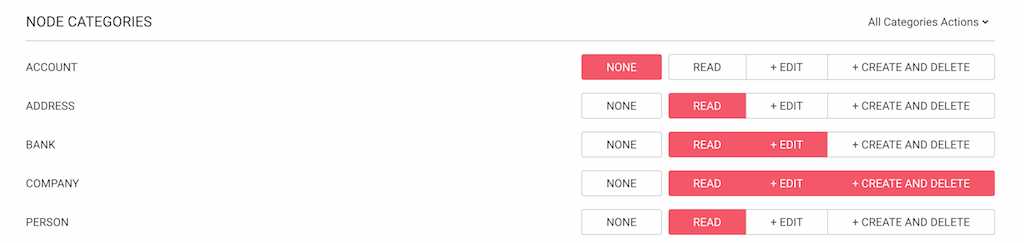
Foo belong to the groups Accounting and SalesAccounting has NO ACCESS access right on node-category CONTRACTSales has EDIT access right on node-category CONTRACTAs a result: user Foo has EDIT access on node-category CONTRACT
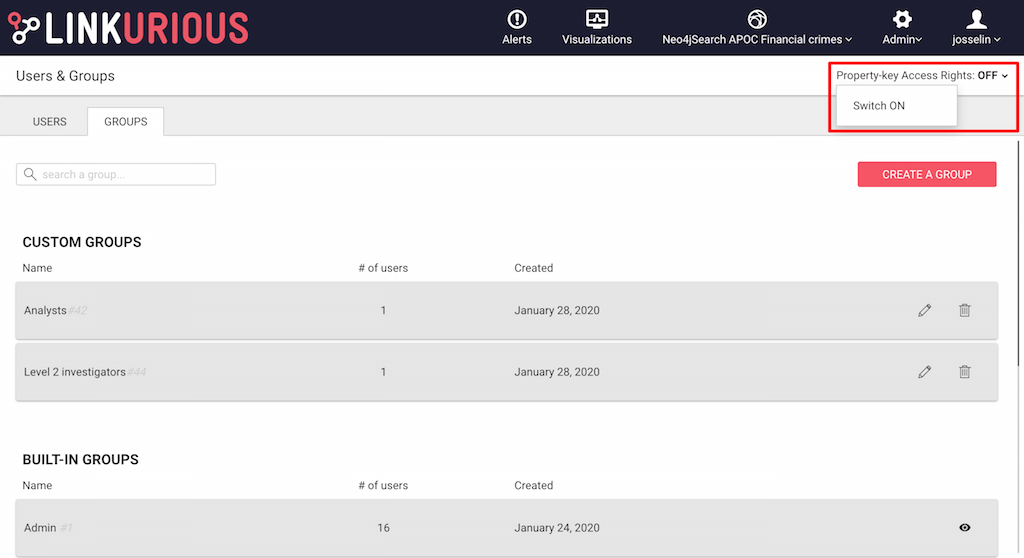
To define property-key access rights, the administrator needs to create (or edit) a custom group: after the access-rights configuration page, with the property-key access rights feature switched on, a second panel will be displayed.
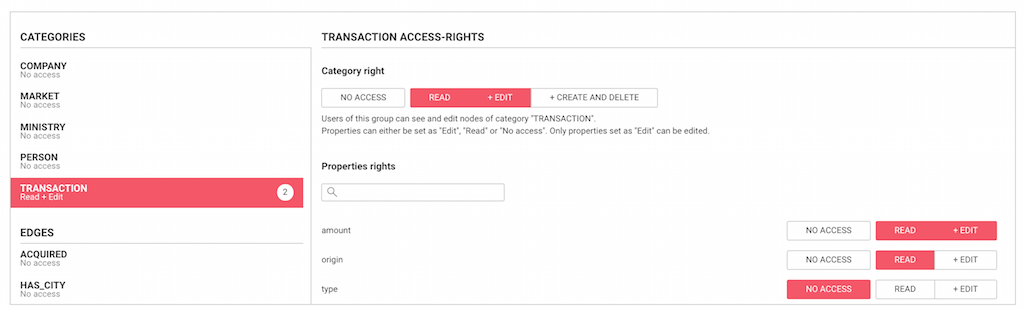
From here:
For each node category (resp. edge type), the administrator is able to set one of the following access-rights (exactly the same as for Standard access rights):
NONE: The user can't access (search or display) nodes (resp. edges) of that category (rest. type).READ: The user can search display nodes (rest.edges) of that category (resp. type).EDIT: The user can edit properties of nodes (rest. edges) of that category (resp. type).CREATE AND DELETE: The user can:
For each property the administrator is able to set one of the following access rights:
NO ACCESS: neither the property nor its value can be seen by this user group.READ: the property value is displayed to this user group but cannot be edited.EDIT: the property value is dipsplayed to this user and can be edited.Access rights are cumulative (see example below).
Foo belong to the groups Accounting and SalesAccounting has:
READ access right on node-category COMPANYREAD access right on the property address of the category COMPANYSales has:
EDIT access right on node-category COMPANYNO ACCESS access right on the property address of the category COMPANYAs a result, user Foo has:
EDIT access right on node-category COMPANYREAD access right on the property address of the category COMPANYThe Guest mode is a way to share graphs with people who do not have an account on Linkurious Enterprise.
Key characteristics:
Standard user interface:
Guest mode user interface:
By default, the Guest mode is disabled. Enabling the Guest mode is done on a per-source basis so that you can manage the access rights associated with the Guest mode at the source level.
Enabling it is a 3-steps process:
guest@linkurio.us. By default it is not associated
with any user group. Assign the Guest user
to the Read-Only group, or any custom group if you need to restrict
its rights (see the security warnings below).Once enabled, the Guest mode is available at http://your-domain.com/guest
(replace your-domain.com with the actual host and port of your server).
By default, guest users won't be allowed to search, export and use the design, filter and edge grouping panel.
If you want to allow guest users to use these features, you can go to the Configuration screen (Menu > Admin > Configuration) and, under the Guest Mode configuration, change the following values:
uiWorkspaceSearch (default false): Whether to allow to searchuiExport (default false): Whether to allow the exportuiLayout (default simple): Whether to allow guest users to have the same UI for layouts as logged-in users (regular), a simpler UI (simple) or no possibility to layout at all (none)uiDesign (default false): Whether to allow the design paneluiFilter (default false): Whether to allow the filter paneluiEdgeGrouping (default false): Whether to allow the edge grouping panelAll people who have access to /guest will be able to browse the whole
database (in read-only mode), even if nobody has explicitly shared a
specific visualization with them. You may want to check who has access
to /guest before enabling the Guest mode.
If you have assigned the Guest user to the Read Only built-in user
group, all node categories and edge types will be available to see by
the people who can access /guest. If the database contains sensitive
data, you should create a custom group
with limited rights on the data and assign the Guest user to that group.
Even if the Guest user is assigned to a group that has Write or Delete permissions, Guest mode users will not be able to write or edit data.
When initialized with a visualization, the Guest mode allows the user to expand the graph beyond the content of that visualization. Consider restricting the Guest user access rights if that is an issue.
Accessing /guest directly will return an empty workspace.
Using parameters in the URL you can populate the Guest mode workspace with:
/guest?populate=visualizationId&item_id=123/guest?populate=nodeId&item_id=123/guest?populate=expandNodeId&item_id=123/guest?populate=searchNodes&search_query=paris&search_fuzziness=0.8/guest?populate=queryId&item_id=123/guest?populate=queryId&item_id=123&query_parameters={"param1":"value1"}The Guest user sees the current state of a visualization. Any change to a visualization from an authenticated user will be automatically applied to the public link shared to the Guest user.
Linkurious Enterprise uses a data schema to deliver some of its features. However, most graph databases are schema-less. As a consequence, Linkurious Enterprise automatically detects the data schema from each data-source. The automatically detected schema is:
The schema can be extended manually. An administrator can:
The schema has two modes:
The Partial mode is flexible and incremental, whereas the Strict schema is stable and normative. Therefore the Partial mode is a better fit in early projects when the data schema is poised to change. The Strict mode is a better fit for production-ready projects that require a more controlled environment.
IMPORTANT
Statements made in the schema DO NOT alter the data in the database:
- Setting a property type in Linkurious Enterprise will not change the type of the corresponding values in the graph database (see section about the property types).
- Switching a node-category, edge-type or property on/off in Linkurious Enterprise will not remove or change the data stored in the graph database.
- Switching to strict mode in Linkurious Enterprise will not remove or change the data stored in the graph database.
The schema can be reached through the Admin menu.
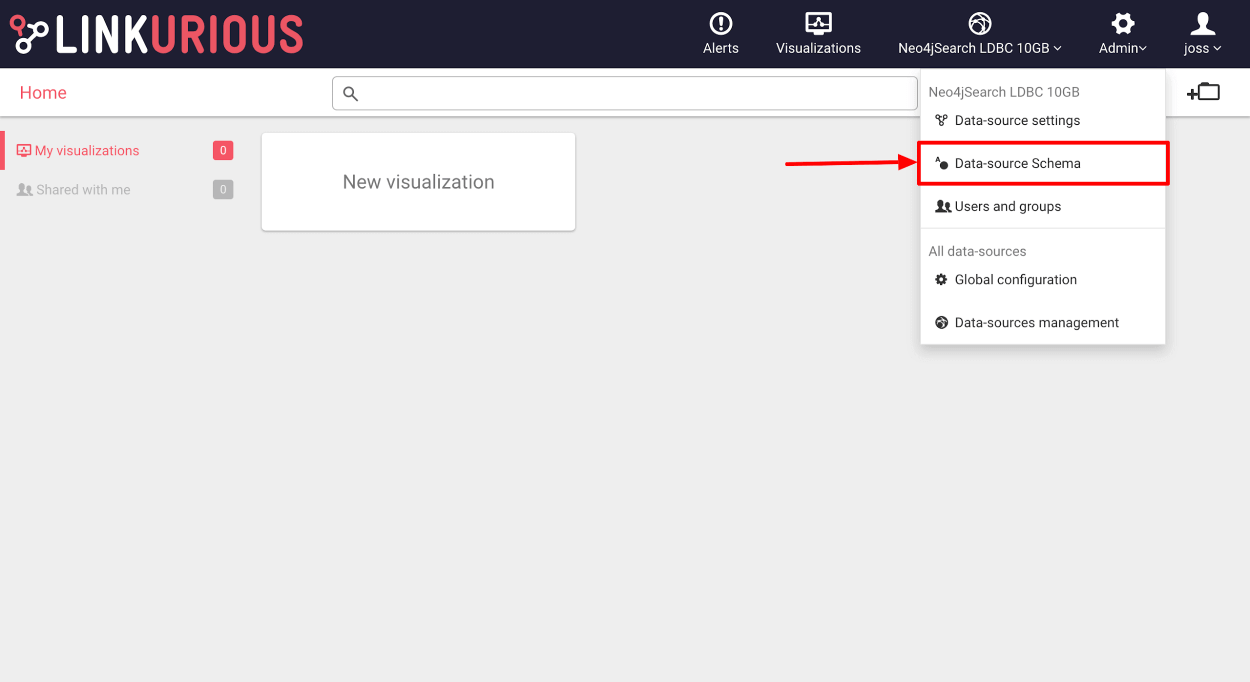
If this is the first time you access the feature, you will be prompted to "sample" the database. Linkurious Enterprise will take a few seconds / minutes to go through a sample of the database and build a more complete schema.
The schema is presented as two columns:
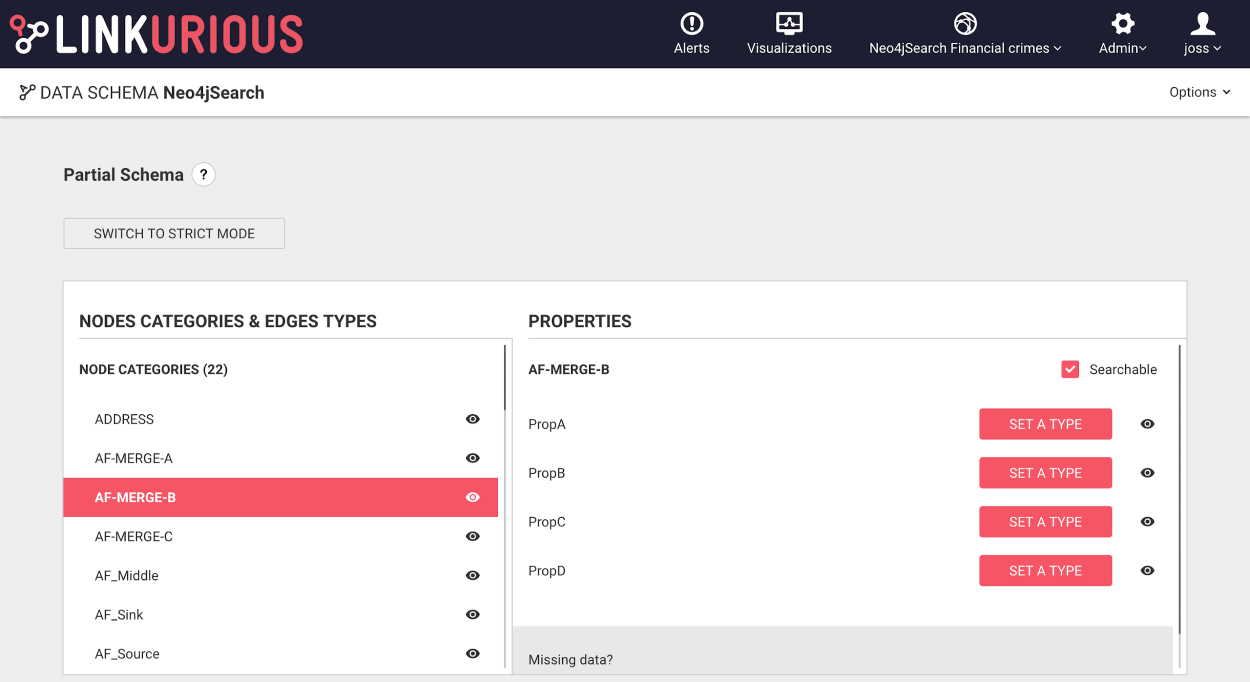
The "eye" icon next to node categories, edge types and properties allows to switch them on or off. See the dedicated section for more details.
The schema may be incomplete. Or you may want to add a category, type or property that is not yet in the data. You can create them manually through action links available at the bottom the list.
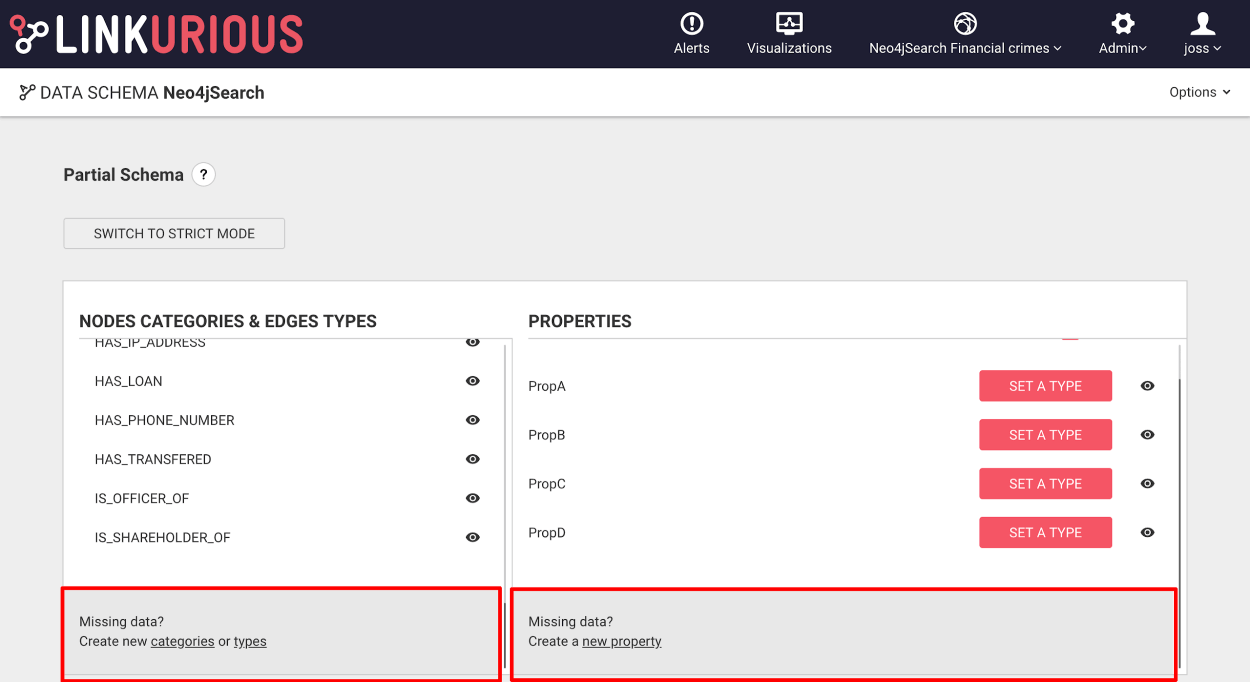
Some node-categories or edge-types are unlikely to be searched for. As a consequence they pollute the search results.
You can remove them from the search by un-checking the "searchable" option at the top of the right column.
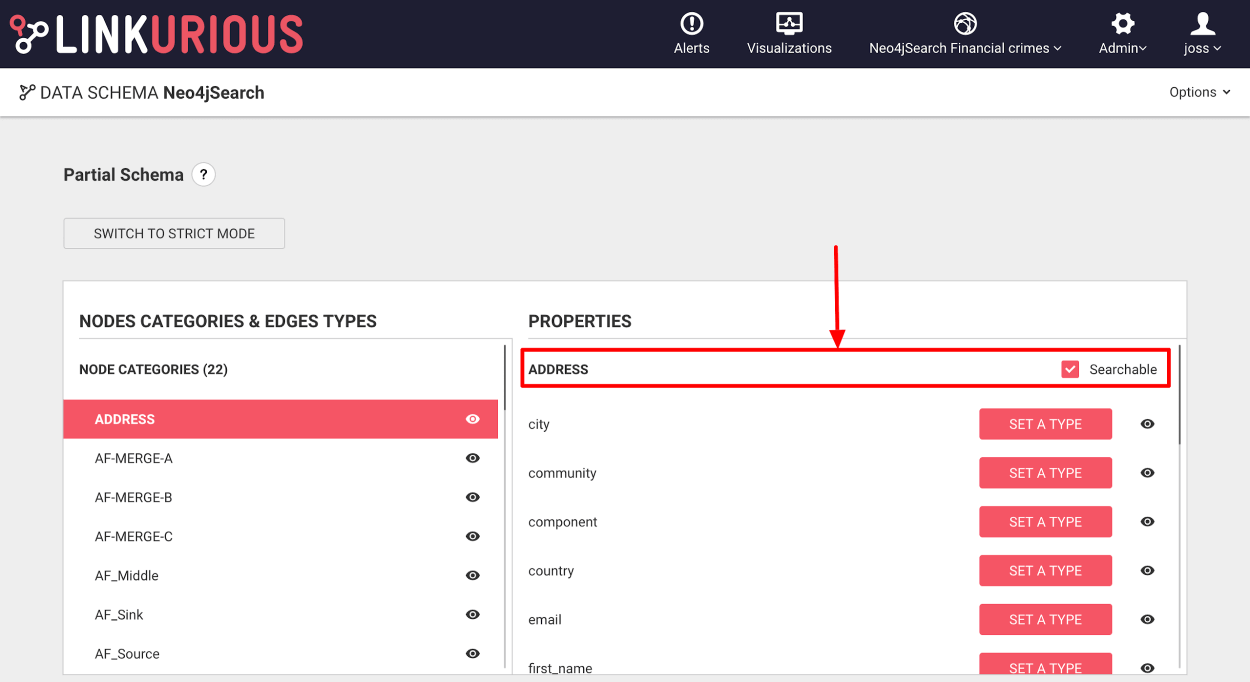
The button "Switch to strict mode" allows you to switch to a strict mode. See the dedicated section for more information.
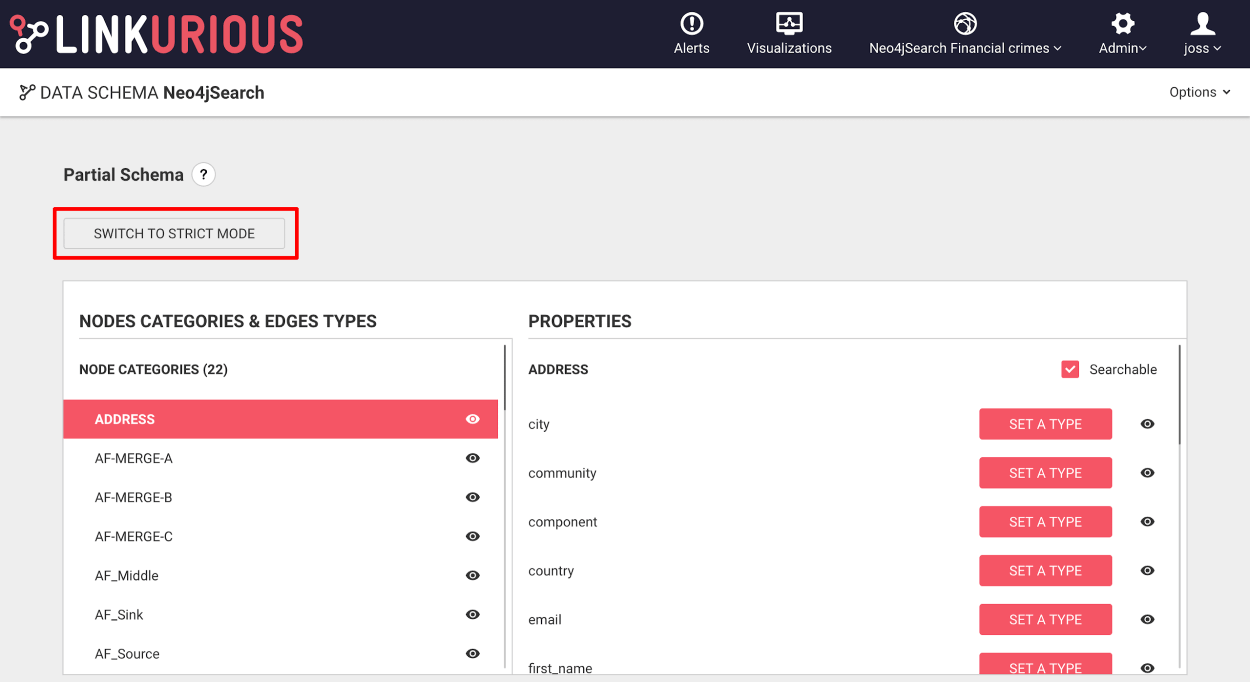
If the schema has changed a lot and you want to start fresh, it is possible to "Reset the schema": this will remove any schema declaration, and trigger a new sampling of the database.
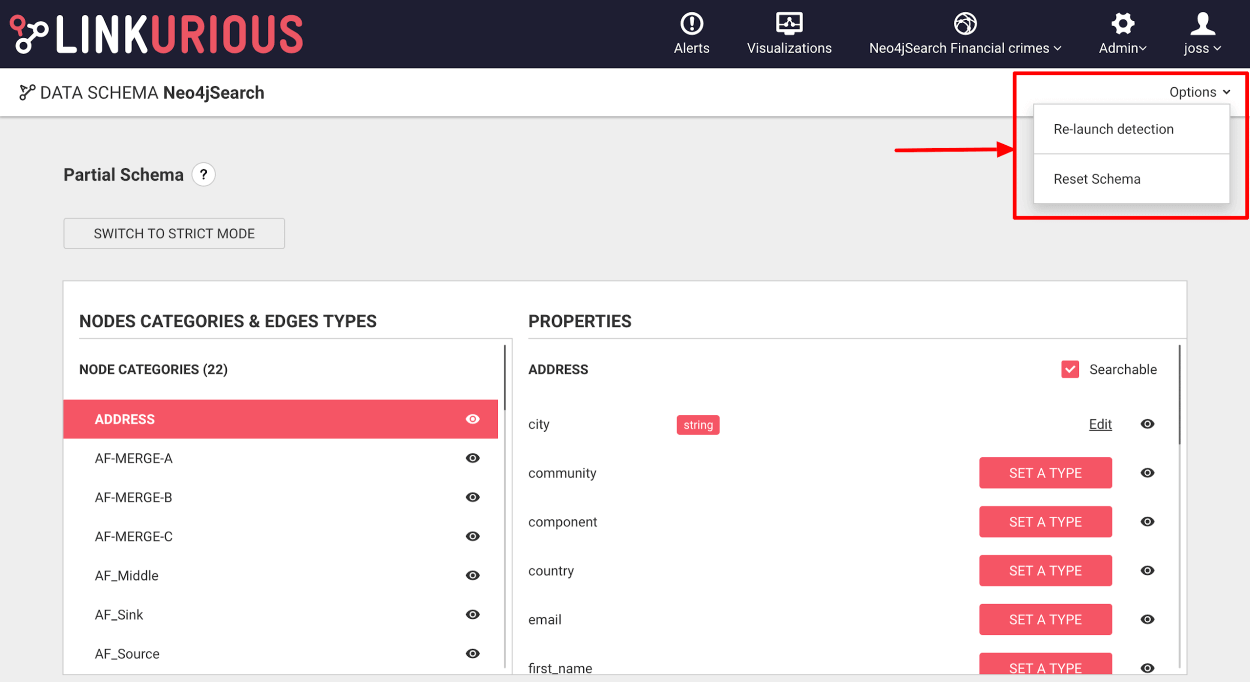
If the schema is too incomplete (due for example to a recent import in the graph database with lots of new node categories / edge types / properties) it's possible to launch manually another sampling round to detect the missing categories / types / properties, using the Re-launch detection option in the Options menu.
The sampling of the database will scan only part of the database. The larger the sample, the more accurate but the longer the detection.
The default setting for the sampling size is 500 nodes per node category, 500 edges per edge type.
You can change this by editing the value of sampledItemsPerType in the Advanced section of the configuration (via Admin > Global configuration).
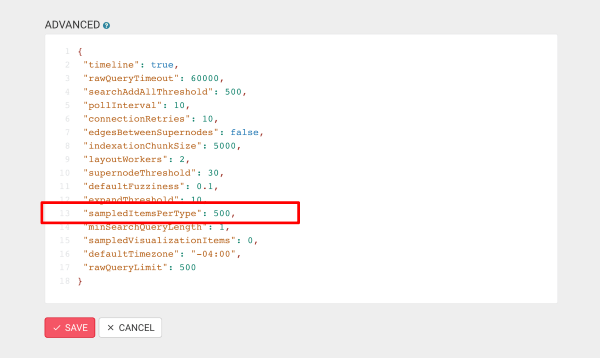
The type of a property can be set by clicking on the "Set a type" button next to a property's name. A popup allows you to choose a type.
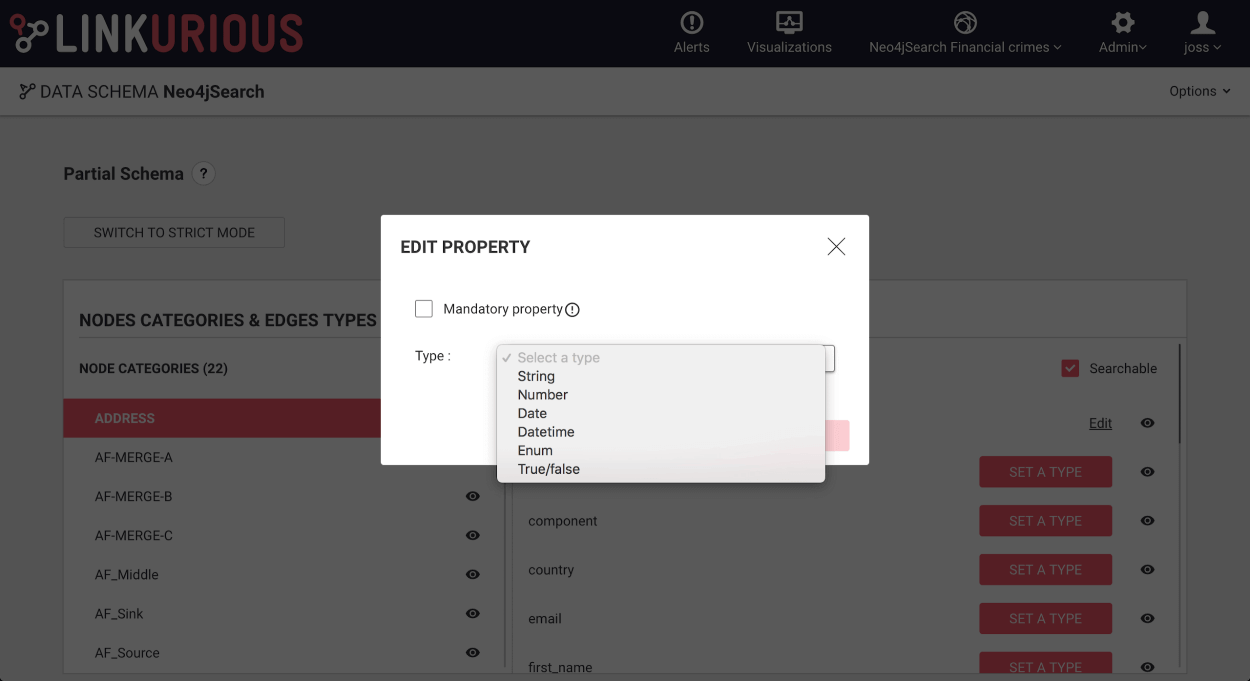
Once a property type has been set, the type is displayed next to the property name, and it is possible to change it using the "Edit" link.

IMPORTANT
Setting a property type in Linkurious Enterprise will not change the type of the corresponding values in the graph database. The consequences are explained below for each property type.
Setting a property type as String does not require any additional information:
Once a property type has been set as a String, all values for that property are processed as a String.
In the Workspace Filter panel:
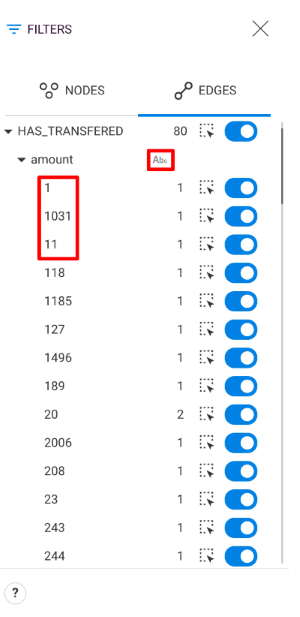
Setting a property type as Number does not require any additional information:
Once a property type has been set as a Number, values for that property fall into 2 categories:
In the Workspace Property panel, invalid values are displayed as string with a warning.
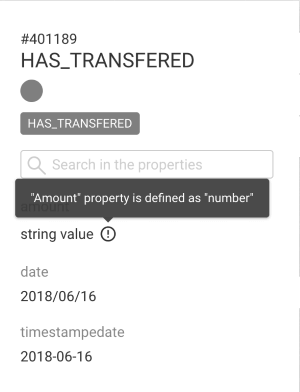
In the Workspace Filter panel:
When editing or creating a node/edge, properties set as Number can only accept a valid number.
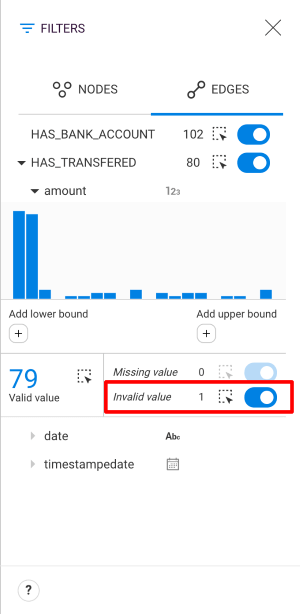
Setting a property type as "Enum" requires to enter a list of authorized values:
, or click on the "Add" button.
Once a property type has been set as Enum, values for that property fall into 2 categories:
In the Workspace Property panel, invalid values are displayed as string with a warning.
In the Workspace Filter panel:
When editing or creating a node/edge, the user pick the value of an Enum property from the list of the authorized values.
Setting a property type as True/false does not require any additional information:
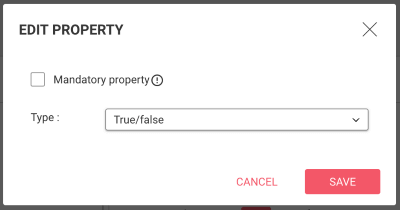
Once a property type has been set as an True/false, values for that property fall into 2 categories:
In the Workspace Property panel, invalid values are displayed as string with a warning.
In the Workspace Filter panel:
When editing or creating a node/edge, the user picks the value of a True/false property from a list containing "true" and "false".
Setting a property type as Date requires to select the storage format of the date in the graph database:
January 1st, 1970 GMT and the date to be encoded.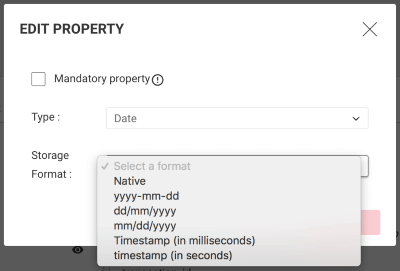
Once a property type has been set as Date, values for that property fall into 2 categories:
In the Workspace Property panel:
Anywhere a date value is displayed (including the Property panel):
In the Workspace Filter panel:
When editing or creating a node/edge, the user picks the value of a Date property from a Date picker.
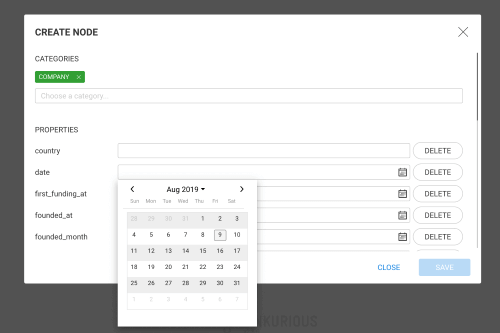
Setting a property type as Datetime requires to select the storage format of the date in the graph database:
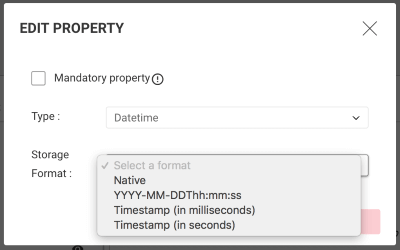
In case the Date-time is stored as Native type in Neo4j, there are 2 possible options:
DateTime object: these object contain an explicit time zone which is used.LocalDateTime object: these objects do not contain an explicit time zone, the default time zone configured in Linkurious Enterprise is assumed.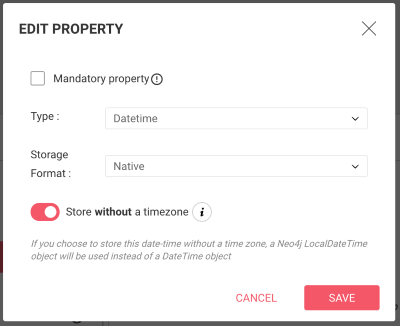
Once a property type has been set as Datetime, values for that property fall into 2 categories:
In the Workspace Property panel:
Anywhere a date value is displayed (including the Property panel):
In the Workspace Filter panel:
When editing or creating a node/edge, the user picks the value of a Datetime property from a Date picker.
Each property can be set as "Mandatory" by clicking the corresponding checkbox in the property type popup.
Consequences of making a property mandatory:
In the Workspace Property panel:
- The property key is always displayed.
- If the item at hand does not have this property, the property is displayed with a warning that the value is missing.
When editing or creating a node/edge, the value of a mandatory property cannot be empty.
When nodes have multiple categories, it is possible that a property can be given 2 different types. For example:
When such conflicts arise:
Switching a node-category (or an edge-type) off is equivalent to setting it to the "No Access" access right for all existing and future User Groups. Nobody will have access to this category / type.
Switching a node-category (or an edge-type) off can be useful when some data is stored in the database for technical reasons but is useless for the users.
The schema allows to switch off nodes-categories and edge-types by clicking on the "eye" icon next to the category/type name. They can be switched back on by clicking on the icon again.
When switching a node-category (or an edge-type) off, a warning is displayed, since it may be used in some existing visualizations, and may impact users.

Properties can be hidden from all users by switching them off. A switched off property:
Switching a property on or off is done by clicking on the "eye" icon next to the property name.
Contrary to the "partial mode", when in "strict mode", you cannot deviate from the data schema when creating or editing a node or an edge.
More specifically, since all properties are typed, you cannot enter a value that is inconsistent with the schema or add arbitrary properties to nodes and edges.
A property must be declared in the schema first, before being available to users.
The schema can be switched to "strict mode" by clicking on the "Switch to strict mode" button.
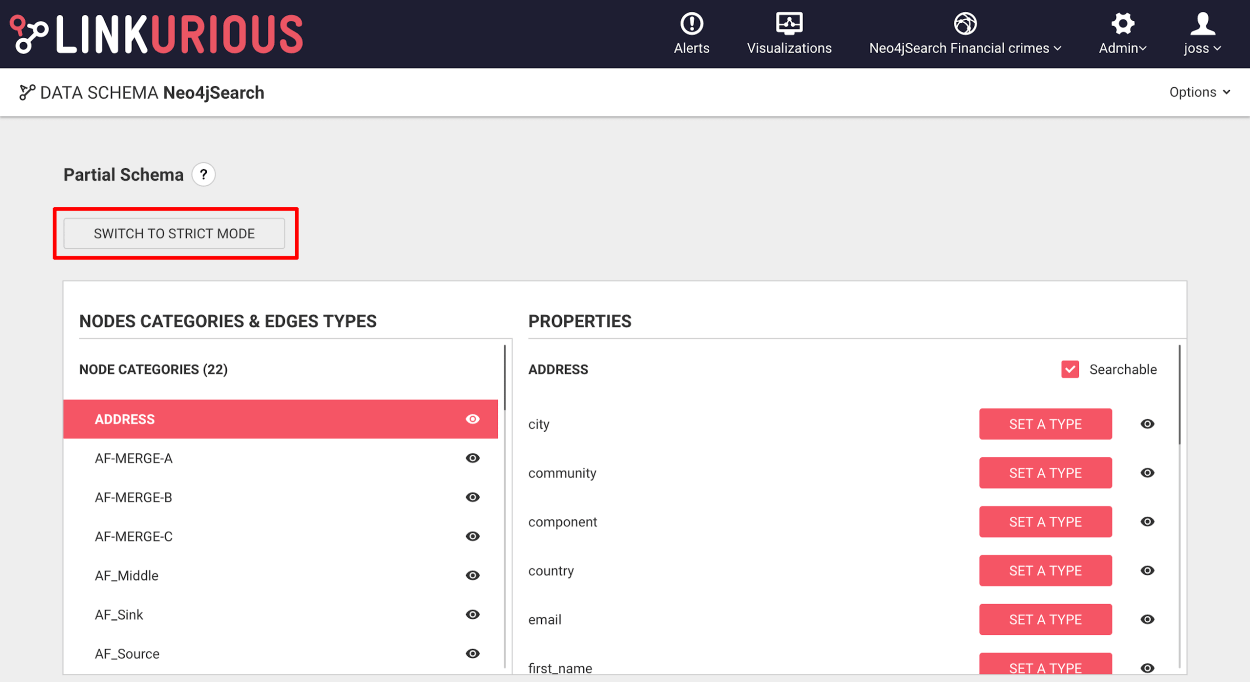
The "strict mode" requires to have types declared for all properties. As a consequence, whe enabling "strict more", all properties that do not have a type are switched off.
When switching to "strict mode", a warning is displayed with the list of properties that are being automatically switched off.

A schema in "strict mode" cannot evolve without an explicit action from the administrator. That means that any node-category, edge-type or property that would be detected after switching to "strict mode" would be added to the schema but be switched off by default.
A schema administrator can add new node-categories, edge-types or properties manually.
A schema in "strict mode" should be stable, so it is non-editable by default. To enable schema edition, the schema administrator needs to click on the corresponding toggle button.
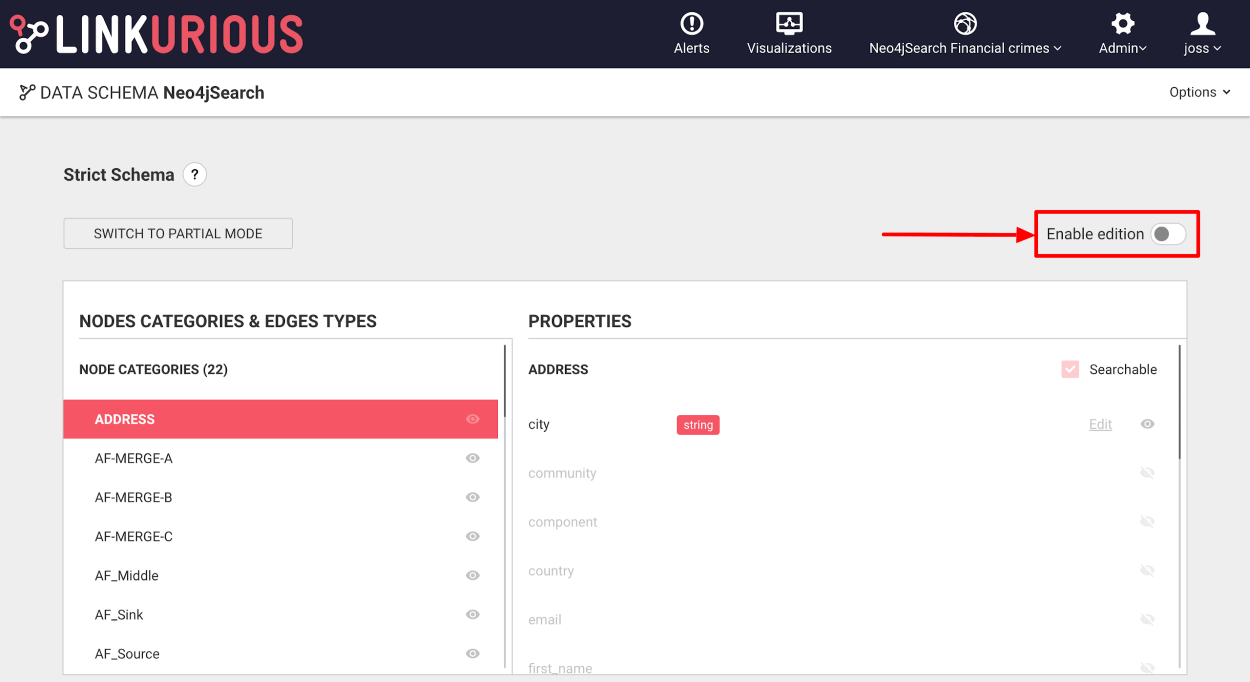
Alerts are a way to watch your graph database for specific patterns and be notified when such pattern appears in the data. A simple triage interface let the users navigate through pattern matches and flag them as confirmed or dismissed.
Alerts are currently only supported via Neo4j.
If you are interested in alerts from other graph vendors, please get in touch.
To create an alert, an administrator needs to:
Using the Run query button, you can preview results for the current query:
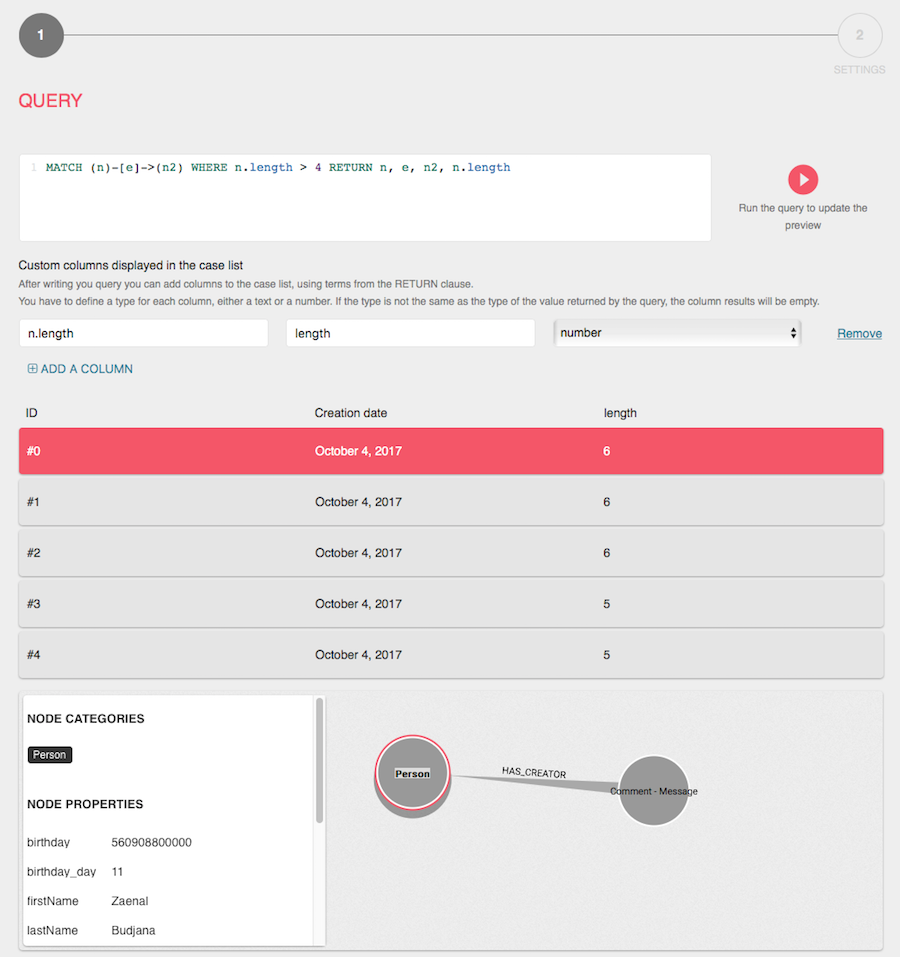
Additional columns can be configured using explicitly returned values, as done here with n.length.
Clicking Next, a secondary configuration page will ask for the name of the alert and the frequency at which the query will be run.
After configuring and enabling an alert, it can be accessed by users in the Alerts panel:
Opening an alerts lists all recent matches, sortable by any column:
Clicking on a match opens it for details:
To enable, disable and customize the alerts behavior see how to configure Linkurious Enterprise.
The following options are available in alerts key:
enabled (default: true): The feature activation parameter. The value false will completely disable the feature preventing even the possibility to define new alerts.
maxMatchTTL (default: 0): The Time To Live is the number of days a result is kept in the new matches section (to be reviewed). If not reviewed before the number of days are elapsed, a result will disappear.
The value 0 means that not reviewed results will disappear only if they aren't matched again at the following execution of the alert check.
maxMatchesLimit (default: 5000): The maximum number of matches returned by a single alert.
maxRuntimeLimit (default: 600000): The maximum execution time (in milliseconds) of a single alert.
maxConcurrency (default: 1): The number of alert queries can be run concurrently. This is useful when you configure multiple alerts and want to prevent them from running at the same time to limit load on the graph database server.
Example of alerts configuration:
alerts: { "enabled": true, "maxMatchTTL": 0, "maxMatchesLimit": 5000, "maxRuntimeLimit": 600000, "maxConcurrency": 1}Linkurious Enterprise allows you to modify the visualizations appearence by modifying the ogma.options settings.
To edit the Ogma settings,
you can either use the Web user-interface
or edit the configuration file located at linkurious/data/config/production.json.
Example configuration:
"renderer": "webgl" "options": "styles": "node": "nodeRadius": 5 "shape": "circle" "text": "minVisibleSize": 24 "maxLineLength": 35 "backgroundColor": null "font": "roboto" "color": "#000" "size": 14 "maxTextLength": 60 "edge": "edgeWidth": 1 "shape": "arrow" "text": "minVisibleSize": 4 "maxLineLength": 35 "backgroundColor": null "font": "roboto" "color": "#000" "size": 14 "maxTextLength": 60 "interactions": "zoom": "modifier": 1382 "pan": "rotation": "enabled": false "backgroundColor": "rgba(240, 240, 240, 0)" Supported ogma.options settings are available here.
In addition to what you find in the Ogma documentation, Linkurious Enterprise allows the following extra configuration keys:
styles.node.nodeRadius (optional) The node radiusstyles.node.shape (optional) The default shape of a nodestyles.node.text.maxTextLength (optional) The maximum length of a node captionstyles.edge.edgeWidth (optional) The width of the edgestyles.edge.shape (optional) The default shape of an edgestyles.edge.text.maxTextLength (optional) The maximum length of an edge captionIn Linkurious Enterprise you can customize the default visual aspect of nodes and edges for new visualizations; your users can then jump head first into the exploration of the data.
Styles can be configured individually by each user using the Design panel. Default values can be configured for all users by an administrator.
Styles belong to one particular data-source. To set the default styles of a data-source, you have two options:

By default, every node category has a pre-assigned color.
Inside Default Styles, the nodes and the edges sections define the
default styles for nodes and edges respectively.
A style rule has the following elements:
index: a unique number >= 0 used to define the order in which rules are applieditemType: node category or edge type the style rule applies to (optional if type is any)type: a value among "any", "novalue", "nan", "range", "is"input (optional): identifier on which the style is computed onvalue (optional): a value to be used by the selector (see the Selectors sections for details)style: the style applied by this rule (see the Styles sections for details)The input field is an array containing a sequence of strings identifying the path to an item in the JSON representation of a visualization object (node or relationship). Supported paths are:
"properties": is the container of all the properties of a visualization object. To identify the property called name, the input value should be ["properties", "name"]."statisics": is the container of the internal statistics computed by Linkurious Enterprise on a a visualization object. Current available statistics are:
"degree": defined a node, represents the number of nodes connected through any type of relationship (in case of supernode, the value is not defined). To access this attribute, the input value should be ["statisics", "degree"].For example:
"index": 3 "itemType": "COMPANY" "type": "is" "input": "properties" "name" "value": "linkurious" "style": "color": "blue" The above rule will apply the style {"color": "blue"} to all nodes
with category "COMPANY" where the name is "linkurious".
"index": 4 "type": "range" "itemType": "COMPANY" "input": "statistics" "degree" "value": ">": 20 "style": "size": "150%" "index": 5 "type": "novalue" "itemType": "COMPANY" "input": "statistics" "degree" "style": "size": "200%" The above rule will apply the style {"size": "150%"} to all nodes with category "COMPANY" that are
connected to more that 20 other nodes and the style {"size": "200%"} to all supernodes with category "COMPANY"
indexhas to be unique. It is currently required for technical reasons. This will be made more user-friendly in future releases.
The selector is used to specify to which items the style is applied to.
For example, you can configure all the "COMPANY" founded more than 12 years ago to have a particular
style. To do so, we use a style rule with a range type and with value:
">": 12The overall style rule will look like the following (assuming we want to color the nodes in red):
"index": 3 "type": "range" "itemType": "COMPANY" "input": "properties" "age" "value": ">": 12 "style": "color": "red" For range queries you can use one or more among the following operators: >, <, >=, <=.
range: matches numerical values that are contained in the range defined in the value parameter, e.g.
{"<=": 12} means "smaller or equal to 12"{">": 0, "<": 10} means "between 0 and 10 excluded"any: matches any value
is: matches all values that are equal to the value parameter, e.g:
"type": "is" "input": "properties" "name" "value": "linkurious" // .. novalue: matches values that are null, missing or contain an empty string
nan: matches values that do not contain a numerical value (Not A Number)
In addition to
type,inputandvalueyou must always specifyitemTypeto filter by node category or edge type except iftypeisany.
Set under the style property key an object with one key, color, e.g:
"style": "color": "blue" // or "#0000FF", "rgba(0, 0, 255, 1)" propertyName in our case):"style": "color": "type": "auto" "input": "properties" "propertyName" The color style for nodes and edges has the same format.
For nodes, set under the style property key an object with one key, size, e.g:
"style": "size": "220%"For edges it is quite similar: set under the style property key an object with one key, width, e.g:
"style": "width": "220%"Set under the style property key an object with one key, shape.
For nodes, set the shape of the node.
Possible values are: "circle" (default), "cross", "diamond", "pentagon", "equilateral", "square" or "star".
"style": "shape": "star" // "circle", "cross", "diamond", "pentagon", "equilateral", "square" or "star" 
For edges, set the shape of the edge.
Possible values are: "arrow" (default), "dashed", "dotted", "line" or "tapered".
"style": "shape": "dotted" // "arrow", "dashed", "dotted", "line" or "tapered" 
You can host your custom icons in Linkurious Enterprise itself by storing them in the folder
located at linkurious/data/server/customFiles/icons.
Users will find them in the Design panel:
![]()
If you want to edit style rules manually, the style rules to access these images would look like:
"style": "image": "url": "/icons/company.png" Nodes can be filled with an image if one of their property is an URL to an image. Available image formats are PNG, JPG, GIF, or TIFF.
The following style will set an image:
Example:
"style": "image": "url": "http://example.com/img/company.png" To assign dynamically an image to a node,
for example if the logo is stored in a node property called "logo_url",
you just need to set the following style:
"style": "image": "url": "type": "data" "path": "properties" "logo_url" // change it to the property key where your image urls are stored If you want to resize your images in a node you can you use the additional properties scale, fit and tile, e.g.:
"style": "image": "url": ... // one of the above "scale": 08 // scale the image in the node "fit": false // if true, fill the node with the image "tile": false // if true, repeat the image to fill the node Editing the default styles in the data-source page does automatically change captions for existing users for newly created visualizations. Existing visualizations are not touched.
In Linkurious Enterprise, node and edge captions are the texts displayed next to a node or an edge.
Captions, as for Styles, can be configured individually by each user using the Design panel.
As for Styles, an administrator can set the default values from its own workspace or by editing them from the data-source configuration page.
Inside Default Captions, the nodes and the edges sections define the
default captions for nodes and edges respectively.
Each of these two sections is an object where the keys are node categories or edge types and the values are objects with the following keys:
active: Whether this caption definition is useddisplayName: Whether to prefix the caption text with the node category or edge typeproperties: An array of properties keys that will be concatenated to create the captionsExample:
"defaultCaptions": "nodes": "CITY": "active": true "displayName": true "properties": "name" "COMPANY": "active": true "displayName": false "properties": "name" "country" "edges": "INVESTED_IN": "active": true "displayName": true "properties": "funded_month" CITY and name: "Paris" would have the caption CITY - Paris.COMPANY, name: "Google" and country: "USA" would have the caption Google - USA.INVESTED_IN and funded_month: "2016-04" would have the caption INVESTED_IN - 2016-04.Editing the default captions in the data-source page does automatically change captions for existing users for newly created visualizations. Existing visualizations are not touched.
Linkurious Enterprise supports displaying nodes with geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude) on a map.
Users are able to switch a visualization to geo mode when geographic coordinates are available on at least one nodes of the visualization. The map tiles layer used in geo mode can be customized by users.
By default, Linkurious Enterprise comes pre-configured with several geographical tile layers.
Administrators change the available geographical tile layers by editing the leaflet section in the configuration file (linkurious/data/config/production.json).
The leaflet key is an array of geographical tile layer configurations.
Each entry has the following attributes:
name (required, string): Name of the geo tiles layer.urlTemplate (required, url): Tile URL template with {x}, {y} and {z} parameters ({s} is optional).minZoom (required, number): The minimum zoom level supported by the layer.maxZoom (required, number): The maximum zoom level supported by the layer.thumbnail (required, url): URL of a 128x60 image to be used as a thumbnail for the layers (for user-added layers, the URL is relative to the linkurious/data/customFiles folder).attribution (required, string): The layer copyright attribution in HTML format.subdomains (string): Letters to use in the {s} tile URL template (required if urlTemplate contains {s} ).overlay (boolean): Whether this layer is a base layer (false) or a transparent layer that can be used as an overlay (true).id (string): Unique tiles layers identifier (MapBox only).accessToken (string): Tiles layer access-token (MapBox only).Geographical tile layers and overlay layers can be found at https://leaflet-extras.github.io/leaflet-providers/preview/.
Example configuration:
"leaflet": "overlay": true "name": "Stamen Toner Lines" "thumbnail": "" "urlTemplate": "http://stamen-tiles-{s}.a.ssl.fastly.net/toner-lines/{z}/{x}/{y}.png" "attribution": "Map tiles by <a href="http://stamen.com">Stamen Design</a>, <a href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0">CC BY 3.0</a> — Map data © <a href="http://www.openstreetmap.org/copyright">OpenStreetMap</a>", "subdomains": "abcd" "id": null "accessToken": null "minZoom": 2 "maxZoom": 20 "name": "MapBox Streets" "thumbnail": "/assets/img/MapBox_Streets.png" "urlTemplate": "https://api.tiles.mapbox.com/v4/{id}/{z}/{x}/{y}.png?access_token={accessToken}" "attribution": "Map data © <a href="http://openstreetmap.org">OpenStreetMap</a>, <a href="http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/">CC-BY-SA</a>, Imagery © <a href="http://mapbox.com">Mapbox</a>", "subdomains": null "id": "mapbox.streets" "accessToken": "pk.eyJ1Ijoic2hleW1hbm4iLCJhIjoiY2lqNGZmanhpMDAxaHc4bTNhZGFrcHZleiJ9.VliJNQs7QBK5e5ZmYl9RTw" "minZoom": 2 "maxZoom": 20 Audit trails are detailed logs about the operations performed on your graph databases by your users. Because they have the potential to take up a substantial amount of memory depending on the number of users and the operations performed, they are disabled by default.
Audit trails can be enabled and configured in linkurious/data/config/production.json.
They are found under the auditTrail key, which contains the following options:
enabled (default: false): Whether to enable audit trail recording.logFolder (default: "audit-trail"): Where to store the results of the audit trail. This path is relative to the linkurious/data directory.fileSizeLimit (default: 5242880, i.e. 5MB): Maximum size of one log file in bytes. A new file is created when the limit is reached (i.e. the logs are rotated). This avoids the creation of unworkably large log files.strictMode (default: false): Whether to ensure that each operation has been logged before returning its result to the user. By setting it to true, logging will take place immediately; if false, the operation will be performed and will not be recorded in the audit trail until it is finished. This can have a substantial effect on the responsiveness of the server if, for example, large queries are run.mode (default: "rw", read and write): Which kinds of user operation to log ("r" for READ, "w" for WRITE, "rw" for READ WRITE). Read operations are those that do not make changes to the database. Note that raw queries are considered READ WRITE and will appear in the audit trail whether or not they make changes do the database.logResult (default: true): Whether to include the result of each operation in the log, i.e. whether to return a JSON representation of each node that has been added, updated, deleted, or simply matched. This can have a huge effect on log size: by setting logResult to false, the audit trail will only capture the properties of the nodes requested, the changes made to those nodes, or raw queries, and not the nodes themselves.logPlugins (default: true): Whether to include all requests and JSON responses to plugins in the audit trail.Enabling the audit trail can impact performances negatively.
Here are options to consider to improve performances:
"mode": "w": only log write queries, ignore read queries"logResult": false: only log the query sent by the user, not the response sent by the server"strictMode": false: do not strictly wait for the audit-trail log to be written to response to each user requestThe audit trail log files contain JSON lines in JSONL format.
You can easily bind a log-management system like Logstash to interpret them.
Each log line contains:
mode: "READ", "WRITE" or "READ WRITE".date: The date of the operation (in ISO 8601 format).user: The email of the user performing the operation.sourceKey: The identifier of the data-source the operation was applied to.action: The type of the operation, which is one of:
"getNode""getEdge""rawQuery""createNode""createEdge""updateNode""updateEdge""deleteNode""deleteEdge""getNodesByEdgesID""getAdjacentNodes""getAdjacentEdges""getAllShortestPaths""searchFull""searchDirectory"params: The parameters of the operation.result: The result of the operation (if auditTrail.logResult is set to true in linkurious/data/config/production.json).Lines are written to the log as follows:
"mode":"WRITE""date":"2017-01-09T17:34:07.446Z""user":"simpleUser@example.com""sourceKey":"e8890b53""action":"createEdge""params":"createInfo":"source":4328"target":4332"type":"ACTED_IN""data":"tata":"toto""result":"edge":"id":5958"data":"tata":"toto""type":"ACTED_IN""source":4328"target":4332"mode":"READ""date":"2017-01-09T17:34:07.478Z""user":"simpleUser@example.com""sourceKey":"e8890b53""action":"getNode""params":"id":4330"result":"node":"id":4330"data":"tagline":"Welcome to the Real World""title":"The Matrix""released":1999"nodeNoIndexProp":"foo""categories":"Movie""TheMatrix""mode":"READ""date":"2017-01-09T17:34:07.507Z""user":"simpleUser@example.com""sourceKey":"e8890b53""action":"getEdge""params":"edgeId":5950"result":"edge":"id":5950"data":"edgeNoIndexProp":"bar""roles":"Neo""type":"ACTED_IN""source":4313"target":4330"mode":"READ WRITE""date":"2017-01-09T17:34:12.253Z""user":"user@linkurio.us""sourceKey":"e8890b53""action":"rawQuery""params":"query":"MATCH (n:Person) RETURN n""dialect":"cypher""result":"nodes":"id":4357"data":"born":1967"name":"Andy Wachowski""categories":"Person""edges":"id":4359"data":"born":1967"name":"Carrie-Anne Moss""categories":"Person""edges":"id":4360"data":"born":1954"name":"James Cameron""categories":"Person""edges":"id":4361"data":"born":1964"name":"Keanu Reeves""categories":"Person""edges":"id":4362"data":"born":1965"name":"Lana Wachowski""categories":"Person""edges":"id":4364"data":"born":1901"name":"Phillip Cameron""categories":"Person""edges":"id":4365"data":"born":1976"name":"Sam Worthington""categories":"Person""edges":Each line is a JSON objects in the following format (with logResult set to true):
"mode": "WRITE" "date": "2017-01-09T17:34:07.446Z" "user": "simpleUser@example.com" "sourceKey": "e8890b53" "action": "createEdge" "params": "createInfo":"source":4328"target":4332"type":"ACTED_IN""data":"tata":"toto" "result": "edge":"id":5958"data":"foo":"bar""type":"BAZ""source":4328"target":4332The params key contains the parameters of the operation being performed. In this case, the user has run as createEdge action; params then contains the source and target IDs of the edge, as well as the ege type and a data key which holds the properties set on that edge.
result contains a JSON representation of the edge produced by the action. As can be seen, there is a substantial amount of duplication between the information in params and in data. This may not be a consideration with operations on single nodes, but with larger collections can mean that log size increases substantially. Consider the example below:
"mode": "READ WRITE" "date": "2017-01-09T17:34:12.289Z" "user": "user@linkurio.us" "sourceKey": "e8890b53" "action": "rawQuery" "params": "query": "MATCH (n1)-[r:DIRECTED]->(n2) RETURN n1, r" "dialect": "cypher" "result":"nodes":"id":4357"data":"born":1967"name":"Andy Wachowski""categories":"Person""edges":"id":6009"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4357"target":4366"id":6010"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4357"target":4367"id":6011"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4357"target":4368"id":4358"data":"tagline":"Return to Pandora""title":"Avatar""released":1999"categories":"Avatar""Movie""edges":"id":6034"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4360"target":4358"id":4360"data":"born":1954"name":"James Cameron""categories":"Person""edges":"id":6034"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4360"target":4358"id":4362"data":"born":1965"name":"Lana Wachowski""categories":"Person""edges":"id":6020"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4362"target":4366"id":6021"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4362"target":4367"id":6022"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4362"target":4368"id":4366"data":"tagline":"Welcome to the Real World""title":"The Matrix""released":1999"nodeNoIndexProp":"foo""categories":"Movie""TheMatrix""edges":"id":6020"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4362"target":4366"id":6009"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4357"target":4366"id":4367"data":"tagline":"Free your mind""title":"The Matrix Reloaded""released":2003"categories":"Movie""TheMatrixReloaded""edges":"id":6021"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4362"target":4367"id":6010"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4357"target":4367"id":4368"data":"tagline":"Everything that has a beginning has an end""title":"The Matrix Revolutions""released":2003"categories":"Movie""TheMatrixRevolutions""edges":"id":6022"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4362"target":4368"id":6011"data":{}"type":"DIRECTED""source":4357"target":4368In this case, we've used a raw query to read nodes from the database without making any changes to them. The results of the query are returned to us in result, and include a substantial number of nodes and edges. To maximize the usefulness of audit trails and to minimize their footprint, it might be advisable to exclude unnecessary data, including passive queries such as these. Disabling logResult and setting mode to "w" (logging only operations which perform write operations to the database) is one strategy for accomplishing this.